Table of Contents
E-Business: Meaning, features, and Types
E-Business: Introduction
In our daily life, we all use a lot of online shopping apps such as Amazon, Flipkart, E-Bay etc. These websites sold a lot of products. But have you ever wondered, where such products come from? Do these companies, manufacture them?
Well, if we say, in India, there are a lot of Retailers, wholesalers and Business Men, who uses those websites to sell their product. In other words, they use these e-commerce websites in order to sell, promote and expand their business.
Not only, these e-commerce websites, but also personal websites and private applications are also included. Shopping online has become easy for us. There is no need to go everywhere physically, you can shop anything while sitting in our home and enjoy great discounts as well.
So, we can say that E-Business is any type of business transaction, which includes selling goods and providing services to the consumer through the internet.
“Michael Aldrich” is known as the father of E-Business. In 1979, he created the Online Shopping Teleputer Wired City Innovative Information Systems which come to be known as e-commerce. This system enables the online transaction between the consumer and the organization. The term “e-business” first was first introduced in the year 1996. It can be described as the abbreviation for electronic business.
E-Business: Meaning
E-business is a term used to describe transactions in business that are conducted on the internet. So, it is a type of business in which the buyer and seller do not meet in person.
‘E-Business is any type of business transaction, which includes selling goods and providing services to the consumer through the internet.’
Definitions of E-Business
“eBusinesss is the general term for buying and selling process that is supported by electronic means” ~Plilip Kotler
Under the Information Technology Act, 2000, “eBusiness is defined as the transactions carried out by means of electronic data interchange and other means of electronic communication in place of paper-based method of communications.”
Definition by OECD, “eBusiness refers to the commercial transaction between organizations and individuals based on the processing or transmission of the digitalized network, units, text-sound and visual images which are carried out over an open network, or a closed networks with a gateway to open network.“
In the words of the International Fiscal Association, “eBusiness means commercial transactions in which an order is placed electronically and goods or service are delivered in tangible or electronic form.”
According to the Department of Treasure, USA, “eBusiness means consumer and business transactions conducted over a network using computers and telecommunications.”
Features of E-Business
1. E-Business is available everywhere and can be accessed by anyone without being restricted by their local areas. It is possible for a customer to shop from their laptops, computers and smartphones being in any part of the country.
2. E-Business enables a business organization to reach beyond geographic boundaries around the different countries rather than limited to their local area. This enables a company to earn greater profit and expand their business in foreign countries thus increasing the foreign trade of their own country.
3. E-business is available at any time of the day with flexible working hours.
4. E-commerce allows direct communication between the customer and the seller making it interactive.
5. E-commerce websites provide the information of a product in a systematic way. It increases the quality and accuracy of the information available on the global internet thus the company cannot spread ‘fake information’ about their product.
6. The setting cost of E-Business is lesser than traditional business.
7. E-Business technology offers the feature of personalization which means a company can design its marketing message for users based on their past activities and the interests of the user.
8. E-Business has higher risk in terms of Online Transactions.
Merits and Demerits of E-Business
Merits of E-Business:
A few of the benefits that are part of Online Business are as follows:
- Online business is easy to set up. No building like a showroom is required.
- There are no geographic boundaries
- Much less expensive than traditional business
- There are business hours that are flexible.
- Marketing strategies cost less
- Online businesses receive subventions from the government
- There are a few integrity and security concerns
- There isn’t any personal touch.
- Seller and buyer don’t get along
- The delivery of items requires a certain amount of time.
- There is a possibility of a transaction risk
- Anyone can purchase anything at any time from anywhere.
- The risk associated with transactions is higher than that of traditional business
Demerits of E-Business
1. Lack of personal touch. A customer cannot touch or check the product by their hand.
2. Transportation risk.
3. There is a risk of online fraud or scams. There are a lot of people who scam through online business.
4. It is easier for hackers to get your financial details. It has a few security and integrity issues.
Types of e-Commerce
- B2B (Business-to-Business)
- B2C (Business-to-consumer)
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer)
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business)
- C2A (Consumer-to-Administration)
- B2A (Business-to-Administration)
- Intra-B Commerce
1. B2B (Business-to-Business)
Business-to-Business (B2B) e-commerce includes any online transactions of products or services that are conducted between companies. Traditional commerce wholesalers and producers typically use this type of e-business.
In other words, B2B is the term used to describe business-to-business relationships between two businesses in which one organization provides services to the other organization.
These business organizations, which are often referred to as the producer of the items that they sell to wholesalers and then wholesalers then re-sell them.
2. B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
B2C e-commerce, also known as B2C mode, consists of selling goods or services to the consumers. In this kind of E-Business, consumers or customers can browse the website and purchase products on the internet using credit cards, Debit cards, cash payments and several other ways.
For example, if we own a business organization and we wish to market our products or services on our website or other online source, then this could be called B2C. B2C model.
One excellent example an excellent example is Amazon as well as eBay. It is good to call their business a Business-to-Consumer model.
3.C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer)
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)is a type of e-commerce that includes any online transactions of products or services between consumers. In general, the transactions are carried out through an outside party that offers the online platform on which the transactions are executed.
C2C online shopping is a transaction between two customers who sell an item using an auction on the internet while the other buyer purchases the item through the highest price.
For instance, let’s assume consumer 1 is looking to sell his/her laptop, and place that laptop on a website such as OLX or eBay and consumer 2 is looking to purchase that laptop.
Thus, customer 2 could call customer 1 and buy his laptop.
4.C2B (Consumer-to-Business)
C2B, also known as consumer-to-business e-commerce is the selling of goods and services to a business through the web.
In this mode of e-business, consumers create commodity, and companies consume that commodity. In C2B it is a total change in the traditional concept of transferring products. This kind of e-commerce is very popular in crowdsourcing-based projects. Many people provide their services or goods accessible for purchase to companies that are looking for these types of products or services.
For instance, a consumer puts some of their products or services on the site.
If the product or service add value to the business, then they will purchase these services or products, however, generally speaking, it is the services that they purchase.
Imagine a client is charged 100$ for a certain service. A business would require that service since it will assist them in a way so that they could purchase that service.
When a deal is concluded, the client receives items or services and the consumer receives his payment. A good illustration that illustrates C2B business model is C2B company model can be seen in the freelancing websites like Fiverr, Freelancer
5. C2A (Consumer-to-Administration)
The Consumer-to-Administration model includes all online transactions conducted between individuals and public administration.
Examples of applications are:
- Education – disseminating information, distance learning, etc.
- Social Security through the dissemination of information, making payments, etc.
- Taxes include filing taxes, paying taxes for tax returns, payments, etc.
- Medical – appointment, details about illness, the cost of health care services, etc.
The C2A e-commerce model helps the consumers to post their queries and request information regarding public sectors directly from their local governments/authorities.
It offers a straightforward method of establishing communication between the consumer and the state.
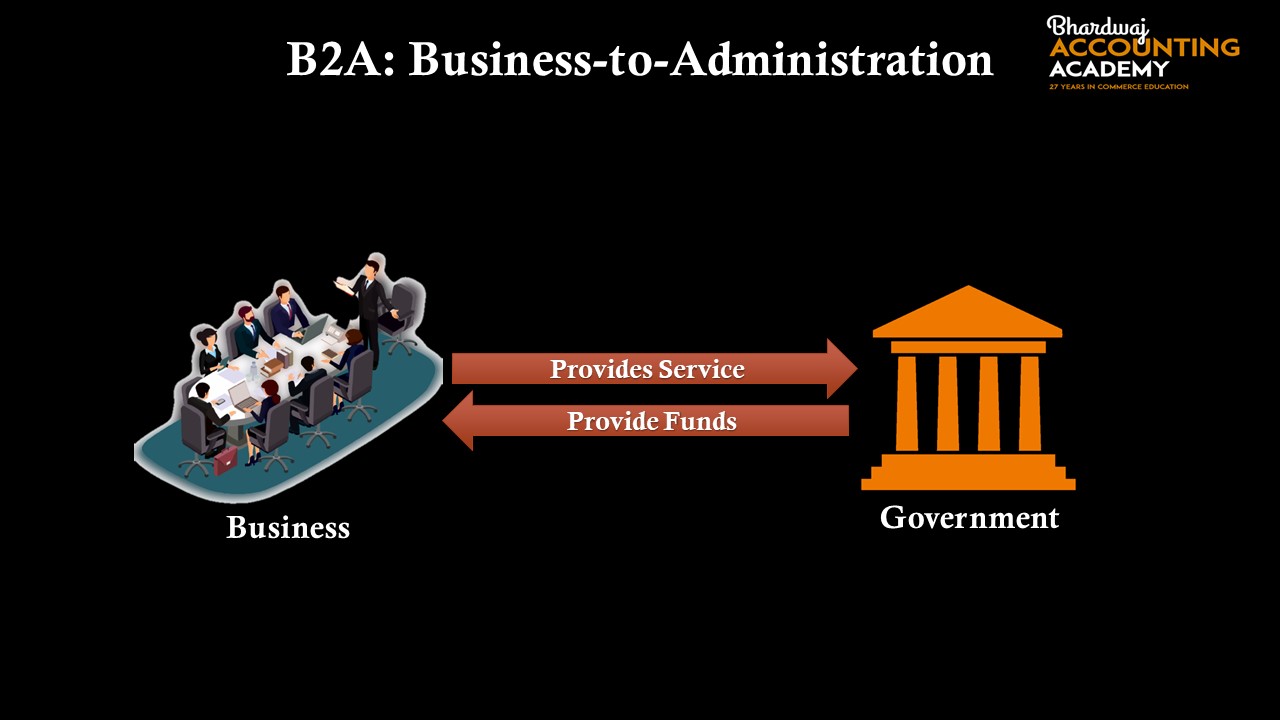
6.B2A (Business-to-Administration)
The term “e-commerce” refers to the entire online transaction between businesses and public administration. This area encompasses a huge amount of many services, especially in the areas like fiscal, social security hiring, documents for legal purposes, registers, etc. These kinds of services have grown significantly in recent years thanks to the investments made in the e-government.
In such type of e-business, the government agencies (administration) make use of central websites to conduct trade or exchange details with a variety of business organizations.
B2A provides a variety of services, including some that include fiscal measures such as legal documents, social security, and various other government-related activities.
The Business-to-administration model is also referred to as Business-to-government (B2G).
Both models of Public Administration (B2A and C2A) are strongly linked to the concept of simplicity and efficiency of the services that are provided publically to the citizens of the state, supported by technologies for information and communication.
7. Intra-B Commerce
Intra-B commerce refers to interaction and dealings among various departments and persons within the firm.
Or
Intra b-commerce refers to transactions between the parties or persons who are part of one firm only.
Intra b-commerce transactions may involve Interaction between two or more departments of one firm.
e-Business Vs Traditional Business
| Basis of Business | E-Business | Traditional Business |
| Definition | E-Business is any type of business transaction, which includes selling goods and providing services to the consumer through the internet. | Traditional business refers to the local business which provides services and products to the local customers. |
| Cost | E-Business is less expensive to start | Traditional Business requires heavy investment to start |
| Ease of Formation | It is easy to form | It is difficult to form |
| Locational Requirement | There is no requirement for location | The preferable location is near raw materials and markets. |
| Risk | High risk due to the lack of personal contact between the parties | Low risk due to the personal contact between the parties. |
| Ease of Going Global | There is more chance of going global | There is less chance of going global |
| Physical Contact | The Consumer did not have physical contact with the product or service i.e. he cannot touch or feel it. | The consumer can touch and check the quality of the product he is willing to buy. |
| Operating Cost | The operation cost is low. | High operation cost due to the investment in production, marketing, etc. |
| Contact with Supplier and customer | There is direct contact between the supplier and the consumer. | It has indirect contact due to intermediaries. |
| Nature of Human Capital needed | Technically and professionally qualified | Mostly semi-skilled and unskilled manpower. |
Business: Meaning, Definition, and objectives
Components of Business Environment CBSE/ISC Class 12
30 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger, Trial balance, and Final Accounts- Project


This site is very helpful.
Very helpful thank you for sharing this much information about E-Business. This is going to help a lot of people and young entrepreneurs too.👾❤️