Table of Contents
Golden Rules Of Accounting
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Traditional or English Approach (Rules of Debit and Credit)-
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Or
3 Golden Rules Of Accounting

Golden Rules Of Accounting-
This approach is also called as the British Approach Or English Approach. This approach is based on the main principle of double entry system (Dual aspect concept).
Dual aspect is the foundation or basic principle of accounting. It provides the very basis for recording business transactions into the book of accounts(Journal). This concept states that every transaction has a dual or two-fold effect and should therefore be recorded at two places. Every debit has a credit and every credit has a debit.
According to this system . We should record both the aspects of a transaction whereas one aspect of a transaction will be debited and other aspect of a transaction will be credited. In the traditional approach, all the accounts are classified into the following two types:-
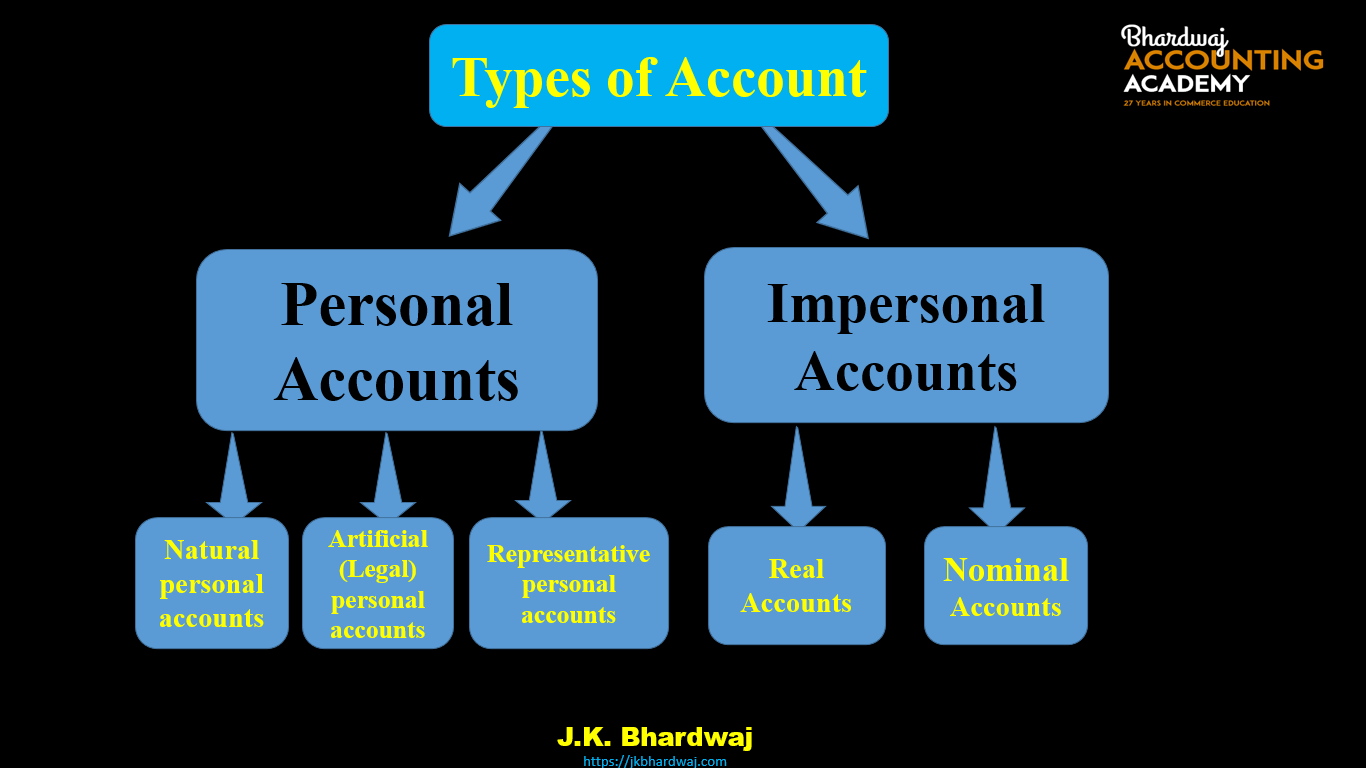
Types of Account-
1. Personal Accounts-
personal accounts are those accounts that relate to persons, Firms, Institutions, and companies like… Account of Jay, Account of Vijay, Account of Mohit, Account of Rachit, Account of Poonam, debtors Account of, creditors account of , Ram&Sons Account of, company Account of, bank Account of, school Account of, government Account of, Capital Account of, Drawings Account of, etc. personal accounts are sub-divided into three categories-
- Natural personal accounts – All those accounts that are related to human beings / Persons are called natural personal accounts. such as – Mohit A/C, Rachit A/C, Mariya A/C, Navjot A/C Capital accounts, , Drawings accounts, Creditors Account, Debtors Account .
- Artificial(Legal) personal accounts- Those Personal accounts that are created artificially by law, such as corporate bodies and institutions, are called Artificial personal accounts. These accounts do not have a physical existence however, they are recognized as persons in business dealings. Those personal accounts which are treated as persons in the eyes of law & have separate legal entity. such as Account of Reliance Industries Ltd, Account of Tata Company Ltd., Account of State Bank of India, Account of Ram & company, Account of Mohan & son’s, Account of BSNL, LIC , Account of School, Account of Government etc.
- Representative personal accounts –Accounts which represent a particular person or group of persons directly or indirectly .For example – Outstanding salary accounts, ( Represent Employee),Prepaid Rent accounts, (Represent Landlord)Advance Income accounts, Accrued Income accounts etc.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Rules of Personal Accounts- Debit the receiver ,Credit the giver.
2.Impersonal Accounts
Impersonal accounts are those accounts which do not related to any persons. Impersonal accounts are sub-divided into two categories-
1.Real Accounts – ( Generally can see, can touch ) Real accounts are those accounts which relate to business property and things which are owned by the business concern. Real accounts include tangible and intangible accounts. For example. – Building account , Land account,Machinery account, Cash account,Furniture account, Computer account,Investment account, Motor account,Fixture and fitting account, Plant account,Goodwill account, Copyright account,Patents account, Trademark account.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Rules of Real Accounts- Debit what comes in,Credit what goes out.
2.Nominal Accounts (Generally can not see, can not touch, can not talk ) – These accounts do not have any existence, form or shape. They relate to Expenses/Losses & Incomes / Gains of a business concern. For example.- Rent account, commission account,Interest account, Discount account, Depreciation account, Bad debts account,Salaries account, Wages account, Charity account, Advertisement Expenses account,General Expenses Account Office Expenses Account, Goods account (purchases, sales, purchases return, sales return, ) etc.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Rules of Nominal Accounts- Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains.
Golden Rules of Debit and Credit in Traditional Approach-
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Personal Accounts- Debit the receiver ,Credit the giver.
Real Accounts- Debit what comes in,Credit what goes out.
Nominal Accounts- Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains.
Also read : Book-keeping meaning definitions and objectives for class 11
Modern or American Approach-
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Or
5 Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Modern Approach is also known as the American Approach. Modern Approach is also known as Accounting Equation Approach/ Balance sheet Equation Approach .
Under this approach transactions are recorded based on the accounting equation. An Accounting equation is based on the dual aspect concept. Dual aspect is the foundation or basic principle of accounting.
It provides the basis for recording business transactions into the book of accounts(Journal). This concept states that every transaction has a dual or two-fold effect and should therefore be recorded at two place.
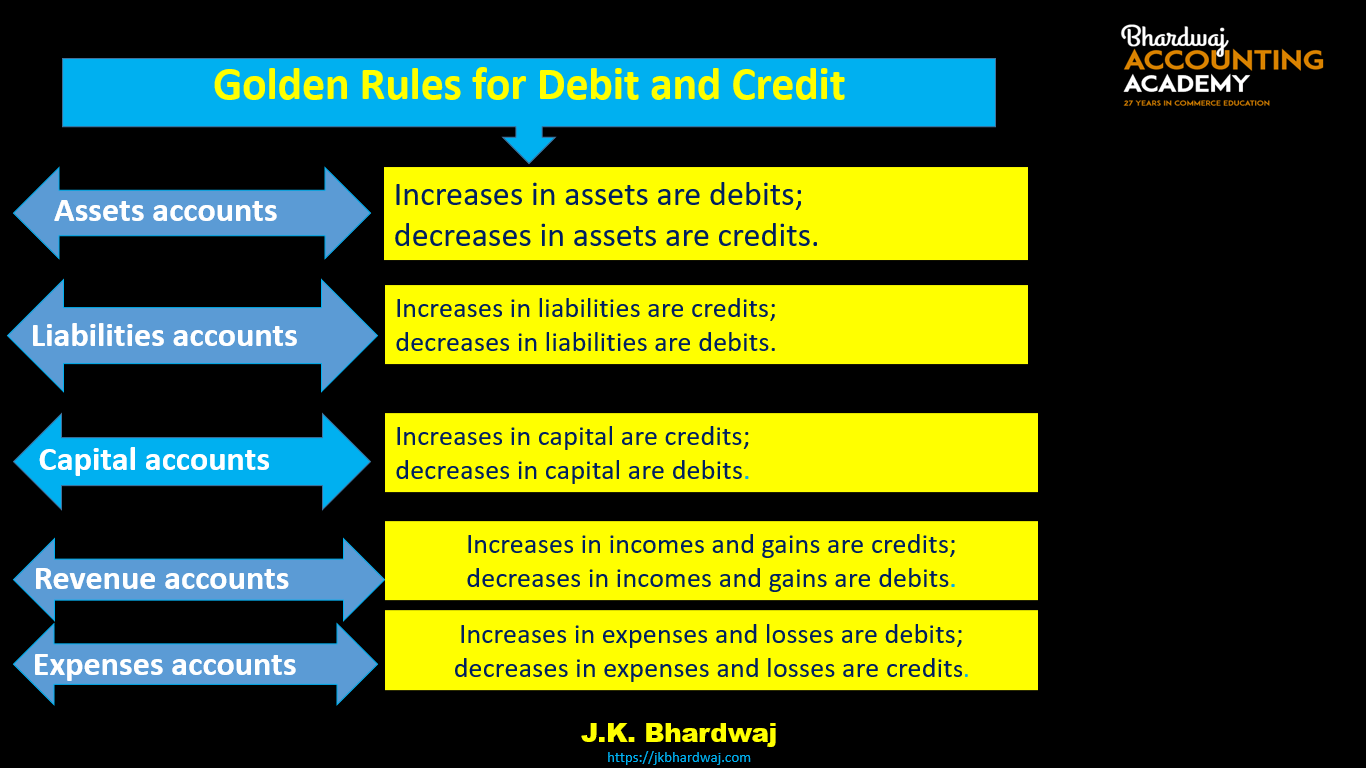
According to American Approach Or Modern Approach Or Accounting Equation Approach Or Balance sheet Equation Approach Accounts are divided into five categories-

1. Assets Accounts
2.Liabilities Accounts
3.Capital Accounts
4.Revenue accounts
5.Expenses accounts
1. Assets Accounts-
Those accounts related to Assets and properties of a business are called assets accounts. Such as Building account , Land account, Plant& Machinery account, Cash account, Furniture account, Computer account , Investment account, Motor account, Fixture and fitting account, Plant account , stock account(Inventory) Debtors account etc.
Rules for Debit and Credit – Increases in assets are debits; decreases in assets are credits.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-

For Example-
1.Building Purchased for cash Rs. 2,00,000 .
Building Account (Assets Account)
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Assets Increase in form of Building
Assets Decrease in form of Cash
Rules- Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Building Account Debit
Cash Account Credit
2.Old Machinery Sold Rs. 60,000 for cash.
Machinery Account (Assets Account)
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Assets Increase in form of Cash
Assets Decrease in form of Machinery
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Cash Account Debit
Machinery Account Credit
2.Liabilities Accounts-
Those accounts related to Liabilities of a business are called Liabilities accounts. Such as Creditors account, Bills payable account, Bank loan account, Outstanding Expenses account, Bank overdraft account etc.
Rules for Debit and Credit- Increases in liabilities are credits; decreases in liabilities are debits.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-

For Example-
1.Loan taken from Jay Rs. 90,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Jay’s Loan Account (Liabilities Account)
Assets Increase in form of Cash
Liabilities Increase in form of Jay’s Loan
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in liabilities are credits;
decreases in liabilities are debits
Cash Account Debit
Jay’s Loan Account Credit
2. Amount paid to creditors Rs. 50,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Creditors Account (Liabilities Account)
Assets Decrease in form of Cash
Liabilities Decrease in form of creditors
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in liabilities are credits;
decreases in liabilities are debits
Creditors Account Debit
Cash Account Credit
3.Capital Accounts-
Capital Accounts refers to the accounts of the proprietors/ partners who have invested money in the business. (Represent Owner/Proprietors or partners).
Capital means that amount or asset which is invested in business by businessman or owner of the business enterprise.
Rules for Debit and Credit- Increases in capital are credits; decreases in capital are debits.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-

For Example-
1.Mr. Mohit started Business with cash Rs. 59,00,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Owner’ Account (Capital Account)
Assets Increase in form of Cash
Capital Increase in form investment by owner
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in capital are credits;
decreases in capital are debits.
Cash Account Debit
Capital Account Credit
2. Amount withdrawn by proprietors for personal use Rs. 10,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Drawing Account (Capital Account)
Assets Decrease in form of Cash
Capital Decrease in form of personal use by owner
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in capital are credits;
decreases in capital are debits.
Capital Account Debit
Cash Account Credit
4.Revenue accounts-
Those accounts related to Income and gains of a business are called revenue accounts. Such as Sales account, commission received account, Discount received account, Rent received account, dividend received account etc.
Revenue means the amount receivable or realised from sale of goods and earnings from interest, dividend, commission, etc.
Rules for Debit and Credit-
Increases in incomes and gains are credits;
decreases in incomes and gains are debits.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-

For Example-
1.Goods sold for cash Rs.90,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Sales Account (Revenue Account)
Assets increase in form of Cash
Revenue increase in form Sale of goods
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in incomes and gains are credits;
decreases in incomes and gains are debits
Cash Account Debit
Sales Account Credit
2.Commission received Rs. 15,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Commission Received Account (Revenue Account)
Assets increase in form of Cash
Revenue increase in form commission received
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in incomes and gains are credits;
decreases in incomes and gains are debits
Cash Account Debit
Commission Received Account Credit
5.Expenses accounts-
Those accounts related to expenses of a business are called expenses accounts. Such as purchaese account, commission account, Discount account, Rent account, Repairs account, General expenses account, Office expenses account etc.
Costs incurred by a business in the process of earning revenue are called expenses.Example for expenses are: Purchase of Goods, Office Expenses, Carriage, Commission to agent, Depreciation, Rent, Wages, Salaries, Interest, Carriage, Manufacturing expenses, Light and water and Telephone, Postage, Administration, Advertisement expenses etc.
Rules for Debit and Credit-
Increases in expenses and losses are debits;
decreases in expenses and losses are credits.
Golden Rules Of Accounting-

For Example-
1.Goods purchased for cash Rs. 50,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Purchase Account (Expenses Account)
Assets decrease in form of Cash
Expenses increase in form of purchase of goods
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in expenses and losses are debits;
decreases in expenses and losses are credits.
Purchase Account Debit
Cash Account Credit
2.Wages paid Rs. 15,000.
Cash Account (Assets Account)
Wages Account (Expenses Account)
Assets decrease in form of Cash
Expenses increase in form Wages
Rules-
Increases in assets are debits;
decreases in assets are credits.
Increases in expenses and losses are debits;
decreases in expenses and losses are credits.
Wages Account Debit
Cash Account Credit
Golden Rules of Debit and Credit in American Approach-
Golden Rules Of Accounting-
Also read : Accounting Equation Class 11
“Accounting is the process of identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, interpreting and communicating financial information to the users for judgment and decision-making”.
Also read : 30 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger, Trial balance and Final Accounts- Project
Ready to test yourself? Perfom live quiz here.

Great article, very informative and detailed
I am continually searching online for posts that can assist me. Thx!
Outstanding post, you have pointed out some great details , I as well think this s a very excellent website.