Table of Contents
Issue of Debentures
The issue of debentures is a way for a company to raise long-term debt capital by issuing a certificate that acknowledges the company’s debt.
Debenture?
When companies need long-term funds for the growth and development of their business, in such a situation, companies take long-term loans from the public and issue certificates for a fixed period under their common seal as proof of loans, these certificates are called Debenture and the holder of such certificate is called Debenture holder.
The debenture is a document issued by a company under its common seal acknowledging the debt and it also contains the terms of repayment of debt and payment of interest at a specified rate.
Debentures are a type of long-term debt instrument that companies use to borrow money. When a company issues debentures, it essentially borrows funds from investors, promising to repay the principal amount at a specified future date and to pay periodic interest on the borrowed amount.
A debenture is a type of long-term debt instrument issued by a company or government entity to raise debt capital. It is a bond or loan that is backed by the issuer’s general creditworthiness rather than specific assets. Debentures typically have a fixed interest rate and maturity date, and investors receive periodic interest payments until the maturity date when the principal amount is repaid.
KEY POINTS:
- The debenture is the most important instrument and method of raising the loan capital by the company.
- A debenture is like a certificate of loan.
- Debentures become a part of the company’s capital structure, it does not become share capital.
- The debenture is a debt acknowledged by a Company.
- As Debentures are in the form of debt, unlike shares they don’t carry voting rights.
Definitions of Debenture?
Section 2(30) of the Companies Act, 2013 define “debenture” which includes debenture stock, bonds or any other instrument of a company evidencing a debt, whether constituting a charge on the assets of the company or not.
“Debenture is a written instrument acknowledging a debt to the Company. It contains a contract for repayment of principal after a specified period or at intervals or at the option of the company and for payment of interest at a fixed rate payable usually either half-yearly or yearly on fixed dates.”
Features of Debenture
1. Debenture holders are the creditors of the company carrying a fixed rate of interest.
2. Debenture is redeemed after a fixed period.
3. Debentures may be either secured or unsecured.
4. Interest payable on a debenture is a charge against profit and hence it is a tax-deductible expenditure.
5. Debenture holders do not enjoy any voting rights.
6. Interest on debenture is payable even if there is a loss.
Types of Debenture
From Security Point of View
(i) Secured or Mortgage Debentures: These are the debentures that are secured by a charge on the assets of the company. These are also called mortgage debentures. The holders of secured debentures have the right to recover their principal amount with the unpaid amount of interest on such debentures out of the assets mortgaged by the company. In India, debentures must be secured.
(ii) Unsecured Debentures: Debentures that do not carry any security with regard to the principal amount or unpaid interest, are called unsecured debentures. These are called simple debentures. Such debentures do not have any charge on the assets of the company.
On the Basis of Records
(i)Registered Debentures: These are the debentures that are registered with the company. The amount of such debentures is payable only to those debenture holders whose name appears in the register of the company.
(ii) Bearer Debentures: These are the debentures that are not recorded in a register of the company. These debentures are payable to bearer of the debentures and transferable by mere delivery. Holder of these debentures is entitled to get the interest. These debentures are also known as unregistered debentures.
On the Basis of Redemption
(i) Redeemable Debentures: These are the debentures that are issued for a fixed period. The principal amount of such debentures is paid off to the debenture holders on the expiry of such a period (Maximum period 10 years from the date of issue). These can be redeemed by annual drawings or by purchasing from the open market.
(ii) Non-redeemable Debentures: These are the debentures that are not redeemed in the lifetime of the company. Such debentures are paid back only when the company goes into liquidation.
On the Basis of Convertibility
(i)Convertible Debentures: These are the debentures that can be converted into shares of the company on the expiry of the predecided period. The term and conditions of conversion are generally announced at the time of issue of debentures.
(ii) Non-convertible Debentures: The debenture holders of such debentures cannot convert their debentures into shares of the company.
Issue of Debentures (Basis of price)
There are three types of debentures issued on the basis of price:
- Issue of Debentures at Par
- Issue of Debentures at Premium
- Issue of Debentures at Discount
Issue of Debentures at par
When Debentures are issued at a price equal to their face value, it is known as Debentures issued at par.
For example – The face value of Debentures ₹10
Issued value of Debentures ₹10
Issue of Debentures at Premium
When Debentures are issued at a price more than their face value, it is known as Debentures issued at Premium.
For example – The face value of Debentures ₹10
Issued value of Debentures ₹12
Note: The securities premium may be collected by the company with application money / Allotment money / First call/Final Call depending upon the terms of the issue of Debentures. If questions are silent regarding the securities premium amount due, it is assumed that securities premium money is due with the allotment money.
Issue of Debentures at Discount
When Debentures are issued at a price less than their face value, it is known as Debentures issued at discount.
For example – The face value of Debentures ₹10
Issued value of Debentures ₹9
Issue of Debentures (Basis of objectives)
Debentures can be issued in three ways depending on the objectives:
1. Issue of Debentures for cash
2. Issue of Debentures for consideration other than cash
3. Debentures issued as collateral security
1. Issue of Debentures for cash:
1. Issue of Debentures for cash at Par and amount receipts in installment:
The following journal entries will be made :
(i)Application money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Application A/c
(Application money received for Debentures)
(ii) Transfer of debentures application money to debentures account on allotment of debentures:
Debentures Application A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Application money transferred to debenture account on allotment)
(iii) Money due on allotment:
Debentures Allotment A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Allotment money made due)
(iv) Money due on allotment is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Allotment A/c
(Receipt of Debenture allotment money)
(v) First call is made:
Debentures First call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(First call money due on …………… debentures)
(vi) Debentures First call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures First call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on call)
(vii) Second and final call is made:
Debentures Second and final call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Second and final call money made due on …………… debentures)
(viii) Debentures Second and final call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Second and final call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on Second and final call)
IllUSTRATION 1.
RACHIT Ltd issued 4,000, 10 % Debentures of ₹ 100 each at par. Amount payable ₹ 20 On application, ₹50 on allotment and ₹ 30 on first and Final call. ₹3 per share. All duly money received on the due date. Pass journal entries in the books of RACHIT Ltd .
SOLUTION:

2. Issue of Debentures for cash at Premium and amount receipts in installment:
The following journal entries will be made :
(i)Application money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Application A/c
(Application money received for Debentures)
(ii) Transfer of debentures application money to debentures account on allotment of debentures:
Debentures Application A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Application money transferred to debenture account on allotment)
(iii) Money due on allotment with premium:
Debentures Allotment A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
To Securities Premium Reserve/Securities Premium A/c
(Allotment money due with premium)
(iv) Money due on allotment is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Allotment A/c
(Receipt of Debenture allotment money)
(v) Money due on the First call :
Debentures First call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(First, call money made due on …………… debentures)
(vi) Debentures First call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures First call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on call)
(vii) Second and final call is made:
Debentures Second and final call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Second and final call money made due on …………… debentures)
(viii) Debentures Second and final call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Second and final call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on Second and final call)
IllUSTRATION 2.
RACHIT Ltd issued 4,000 , 10 % Debentures of ₹ 100 each at 20 % Premium.Amount payable ₹ 20 On application, ₹ 70 on allotment (With Premium) and ₹30 on first and Final call. All duly money received on due date. Pass journal entries in the books of RACHIT Ltd.
SOLUTION:

3. Issue of Debentures for cash at Discount and amount receipts in installment:
The following journal entries will be made :
(i)Application money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Application A/c
(Application money received for Debentures)
(ii) Transfer of debentures application money to debentures account on allotment of debentures:
Debentures Application A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Application money transferred to debenture account on allotment)
(iii) Money due on allotment:
Debentures Allotment A/c Dr.
Discount on issue of debentures A/c Dr
To Debentures A/c
(Allotment money made due and discount allowed)
(iv) Money due on allotment is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Allotment A/c
(Receipt of Debenture allotment money)
(v) First call money due:
Debentures First call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(First, call money due on …………… debentures)
(vi) Debentures First call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures First call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on call)
(vii) Second and final call is made:
Debentures Second and final call A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Second and final call money due on …………… debentures)
(viii) Debentures Second and final call money is received:
Bank A/c Dr.
To Debentures Second and final call A/c
(Receipt of Amount due on Second and final call)
IllUSTRATION 3.
MOHIT Ltd issued 4,000, 10 % Debentures of ₹ 100 each at 10 % Discount.Amount payable ₹ 20 On application, ₹ 40 on allotment (With Discount) and ₹30 on first and Final call. All duly money received on due date. Pass journal entries in the books of RACHIT Ltd.
SOLUTION:

Golden Rules Of Accounting MCQs with solved answers
Issue of Debentures for Consideration Other than Cash
When a company purchases some assets and issues debentures as a payment for the purchase, to the vendors it is known as issue of debentures for consideration other than cash. Debentures can be issued to vendors at par, at premium, and at discount.
Accounting Treatment:
1. For Purchase of Assets on credit
Sundry Assets A/c Dr.
To Vendors A/c
(Purchase of assets on credit)
2. Debentures issued to vendors
(i) Issue of debentures At par to vendor’s
Vendors’ A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Issue of debentures to vendors at par )
(ii) Issue of debentures At discount to vendor’s
Vendors’ A/c Dr.
Discount on issue of debentures A/c Dr.
To Debentures A/c
(Issue of debentures to vendors at a discount)
(iii) Issue of debentures At premium to vendor’s
Vendors’ A/c Dr
To Debentures A/c
To Securities Premium Reserve A/c
(Issue of debentures to vendors at a premium)
IllUSTRATION 4.
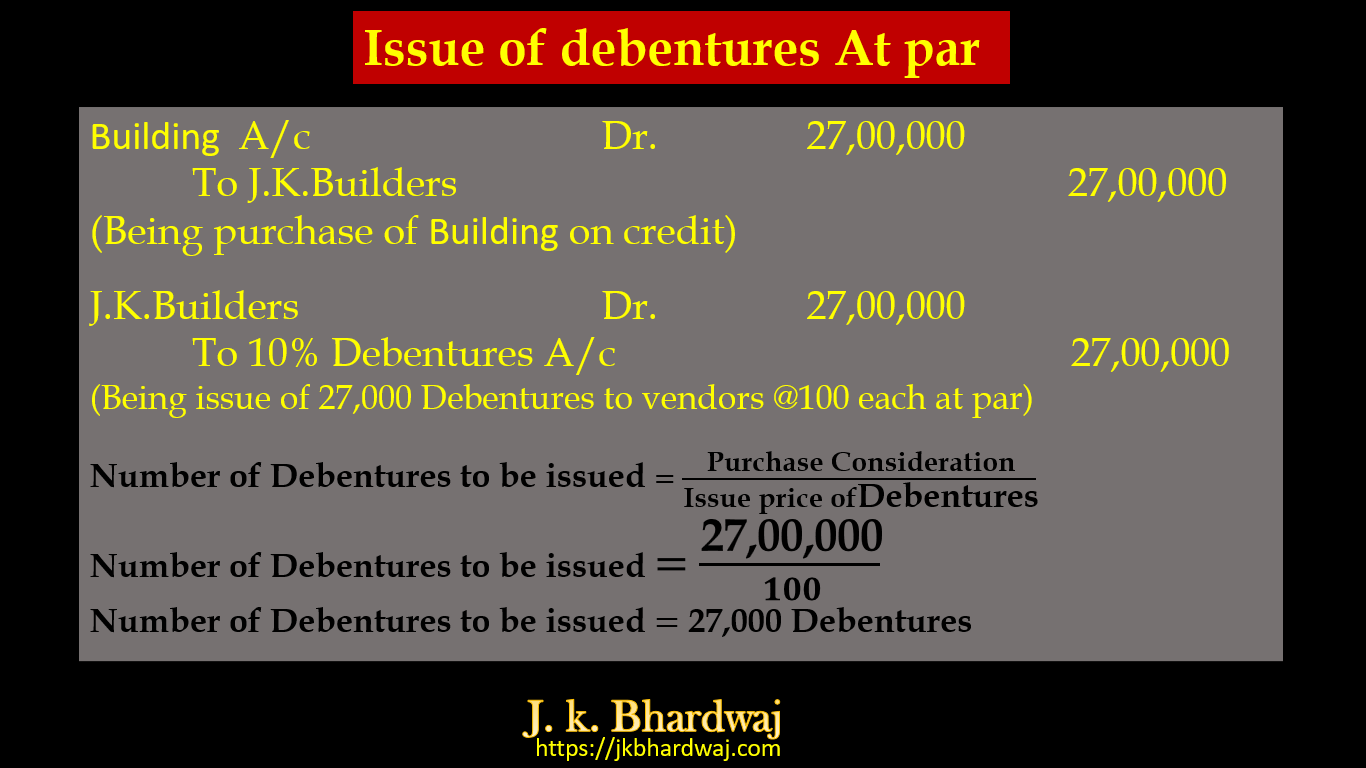
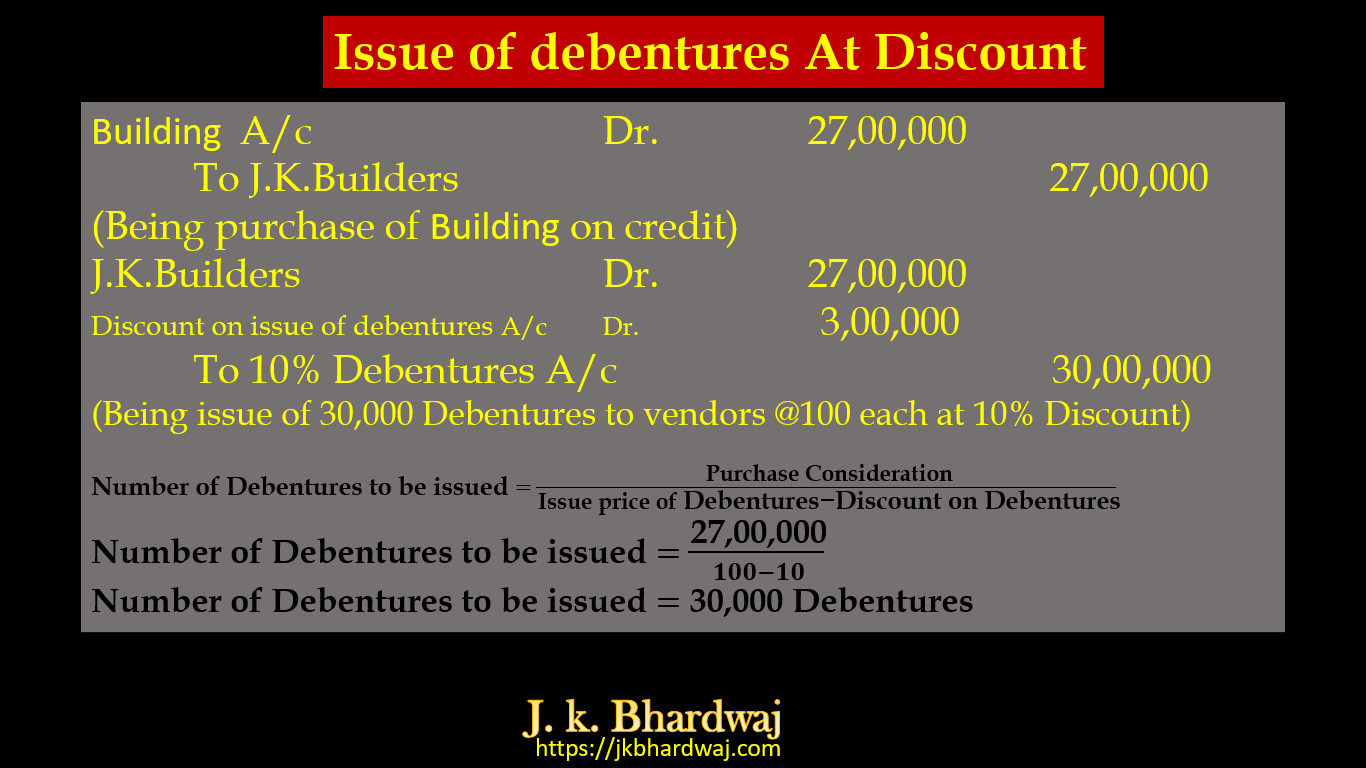
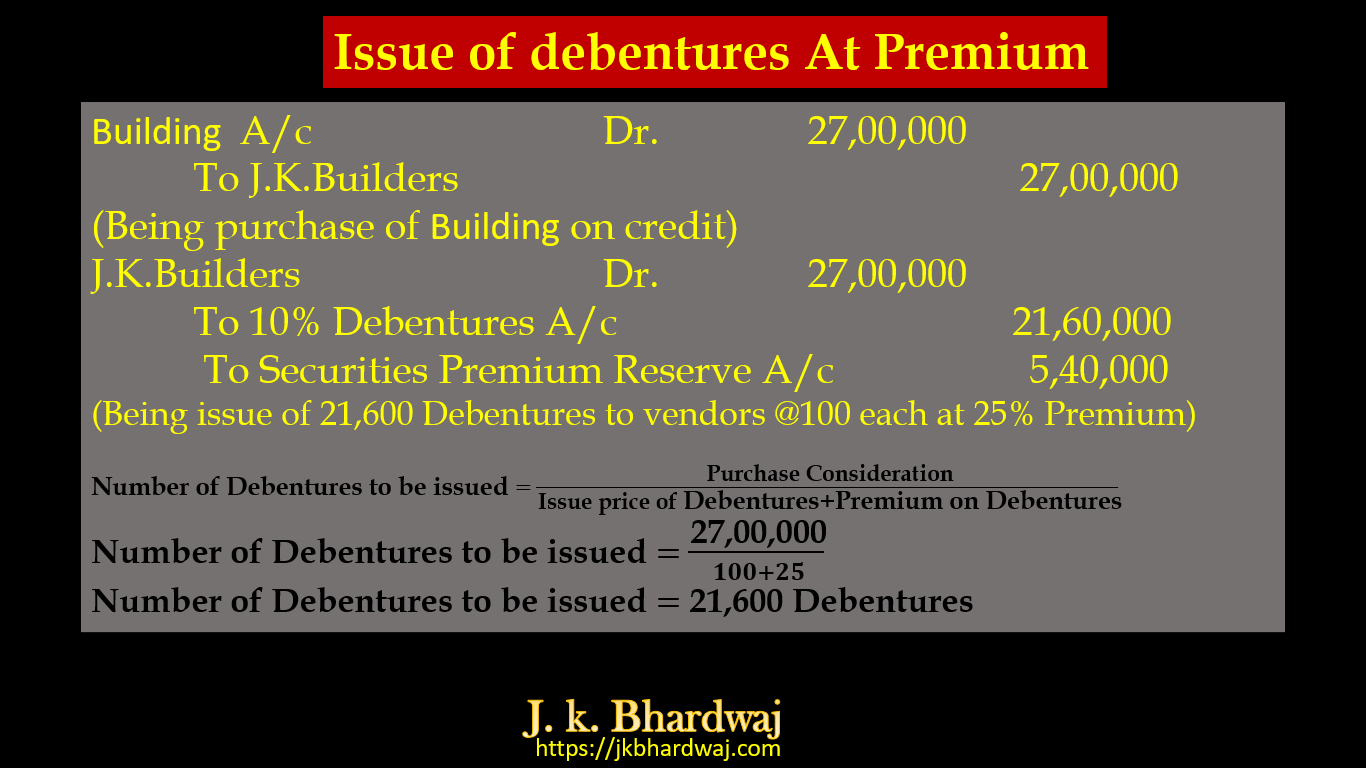
The Hindustan Limited purchased Building on credit from J. k. Builders ₹27,00,000 and issued 10% Debentures of ₹100 each as purchase consideration. pass Journal Entries form the following cases –
(a)If debentures issued at par.
(b)If debentures issued at 10% Discount.
(c)If debentures issued at 25% Premium.
SOLUTION:
(a)If debentures issued at par.
(b)If debentures issued at 10% Discount.
(c)If debentures issued at 25% Premium.
3. Debentures issued as collateral security
Collateral security means security given in addition to the principal security. It is a subsidiary or secondary security. Whenever a company takes loan from the bank or any financial institution it may issue its debentures as secondary security which is in addition to the principal security. Such an issue of debentures is known as the ‘issue of debentures as collateral security.’
Debentures issued as collateral security may or may not be recorded in the books of accounts if an accounting entry is not passed it is disclosed under the loan if an accounting entry is passed it is shown below the loan first as debenture issued and thereafter debenture suspense account is deducted.