Table of Contents
Supply and Its Determinants
Supply
Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity that a firm/producer is willing and able to offer for sale, at each possible price during a particular or given period of time.
Essential Elements of Supply
- Quantities of the commodity
- Willingness to offer for sale
- Price of the commodity
- Particular Period of time
- Supply is a flow concept
Stock
Stock refers to the quantity of a particular commodity that is available with the firm /producer/seller at a particular point of time.
Stock and Supply
- Stock can never be less than the supply.
- Stock indicates a fixed quantity.
- Stock is not part of supply.
- Supply is that part of stock which a producer is willing to bring in the market for sales.
- Stock relates to a particular point of time.
- Stock is not a flow concept
Individual and Market Supply
Individual Supply
Individual Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity that a firm /producer is willing and able to offer for sale, at each possible price during a particular or given period of time.
Market Supply
Market Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity that all the firm/all the producer are willing and able to offer for sale, at each possible price during a particular or given period of time.
Factors Affecting Supply
The factors which affect the Supply for a commodity are known as determinants of supply . A change in any one of these factors will results in change in supply .The Important determinants of supply as follows:-
- Price of the commodity
- Price of Related Goods
- Prices of factor of production/Cost of Production
- State of technology
- Goals or objectives of the firm
- Number of firms
- Means of transportation and communication
- Future Expectations of Rise in Price
- Government Policy
- Agreement among the producer
ALSO READ: DEMAMD AND TYPES OF DEMAND
-
Price of the Commodity-
Own price of the commodity is the most important factor affecting Supply for the given commodity.
There is a direct relationship between the commodity’s price and its quantity Supplied.
When the price of a commodity falls, its SUPPLY falls, and when its own price rises, its supply rises.
The quantity supplied for a product decreases with a decrease in its price and increases with an increase in its price while other factors are constant.
It happens because, at higher prices, there are greater chances of making a profit. It induces the firm to offer more for sale in the market.
-
PRICE OF RELATED GOODS-
As resources have alternative uses, the quantity supplied of a commodity depends not only on its price but also on the prices of other commodities.
An increase in the prices of other goods makes them more profitable in comparison to the given commodity.
As a result, the firm shifts its limited resources from the production of the given commodity to the production of other goods.
For example, an increase in the price of other goods (say, wheat) will induce the farmer to use land for the cultivation of wheat in place of the given commodity (say, rice).
-
PRICES OF FACTORS OF PRODUCTION/COST OF PRODUCTION (INPUTS)-
When the amount payable to factors of production and cost of inputs increases, the cost of production also increases. This decreases the profitability.
As a result, seller reduces the supply of the commodity. On the other hand, decrease in prices of factors of production or inputs, increases the supply due to fall in cost of production and subsequent rise in profit margin. To make ice-cream, firms need various inputs like cream, sugar, machine, labour, etc.
When price of one or more of these inputs rises, producing ice-creams will become less profitable and firms supply fewer ice-creams.
-
STATE OF TECHNOLOGY-
Technological changes influence the supply of a commodity. Advanced and improved technology reduces the cost of production, which raises the profit margin.
It induces the seller to increase the supply. However, technological degradation or complex and out-dated technology will increase the cost of production and it will lead to decrease in supply.
5. GOVERNMENT POLICY (TAXATION POLICY)-
Increase in taxes raises the cost of production and, thus, reduces the supply, due to lower profit margin.
On the other hand, tax concessions and subsidies increase the supply as they make it more profitable for the firms to supply goods.
If tax is imposed by the government on the inputs of a commodity, cost of production will go up. Supply will be reduced. When subsidy is given to the producer, it will encourage them to produce and supply more. Subsidy means a part of the cost of a commodity will be borne by the government.
6. GOALS OR OBJECTIVES OF THE FIRM-
Generally, supply of a commodity increases only at higher prices as it fulfills the objective of profit maximization.
However, with change in trend, some firms are willing to supply more even at those prices, which do not maximise their profits.
The objective of such firms is to capture extensive markets and to enhance their status and prestige.
7. STATE OF TECHNOLOGY-
State of production technology affects the supply function. If advanced technology is used in the country, large scale production is possible. Hence supply will increase. Old technology will not increase the supply.
8. SELLER’S EXPECTATIONS ABOUT THE FUTURE PRICE-
Seller’s expectations about the future price affect the supply. If a seller expects the price to rise in the future, he will withhold his stock at present and so there will be less supply now.
Besides change in price, change in the supply may be in the form of increase or decrease in supply.
9. TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION CONDITIONS-
Improvement in the means of transaction and communication help in maintaining proper supply of the commodity.
Difficulties in transport may cause a temporary decrease in supply as goods cannot be brought in time to the market place. So even at the rising prices, quantity supplied cannot be increased.
SUPPLY SCHEDULE
Supply schedule is a tabular statement showing various quantities of a commodity being supplied at various level of price, during a given period of time.
In the other words-Supply schedule shows the direct relationship between price of the commodity and its quantity supplied.
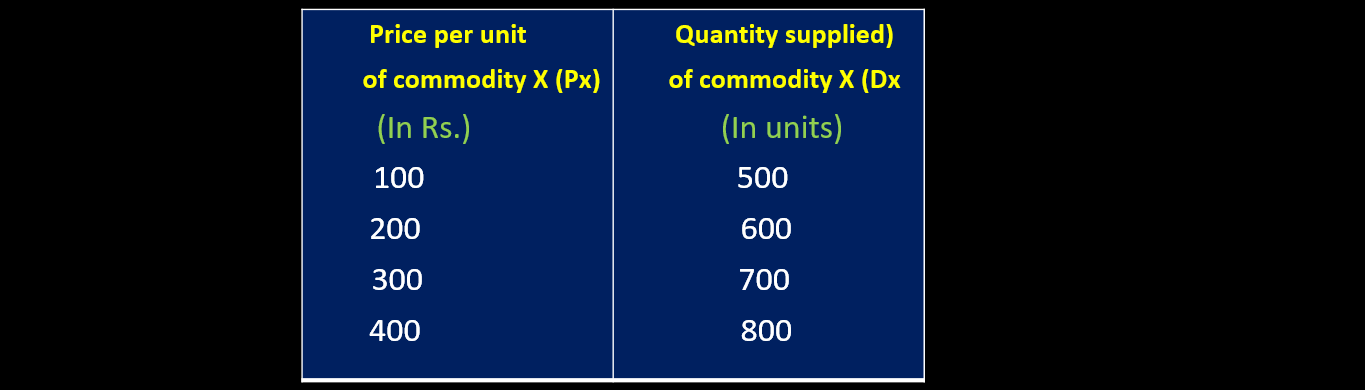
INDIVIDUAL SUPPLY SCHEDULE
Individual supply schedule is a tabular statement showing different quantities of a commodity that a producer is willing to offer for sale at various levels of price, during a given period of time.
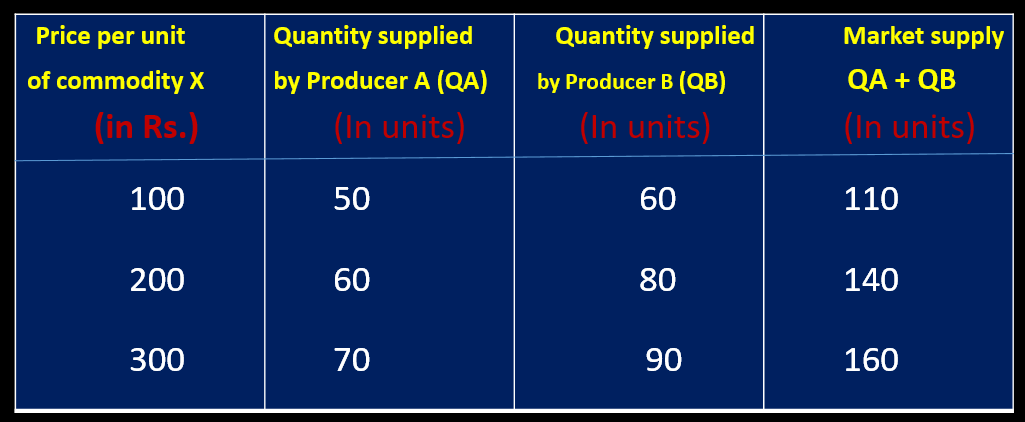
MARKET SUPPLY SCHEDULE
Market supply schedule is a tabular statement showing different quentities of a commodity that all the producers are willing to offer for sale at various levels of price, during a given period of time.
SUPPLY FUNCTION
Supply Function shows the functional relationship (cause and effect relationship) between quantity supplied for a particular commodity and factors affecting supply .
Or
Supply function is an algebraic expression that shows the functional relationship between the supply for a commodity and its various determinants(Factors) affecting supply.
Or
A supply function shows the functional relationship between the quantity supplied and the factors on which supply depends on.
INDIVIDUAL SUPPLY FUNCTION
Individual supply function refers to the functional relationship between individual supply and the factors affecting individual supply.
Sx = f (Px, Pr, F, Go, Te , Gp…)
Sx = Supply for Commodity x
Px = Price of the given Commodity x
Pr = Prices of Related Goods
F = Price of factor of production
Go = Goals of producer
Te = State of technology
Gp = Government policy
MARKET SUPPLY FUNCTION
Market Supply function refers to the functional relationship between market supply and the factors affecting market supply.
Sx = f (Px, Pr, F, Go, Te , Gp, N, Fu, Tc , A…)
Sx = Supply for Commodity x;
Px = Price of the given Commodity x;
Pr = Prices of Related Goods;
F = Price of factor of production
Go = Goals of producer
Te = State of technology
Gp = Government policy
N= Number of firms
F = Future expectation regarding price
Tc = Means of transportation and communication
A= Agreement among the producer
SUPPLY CURVE
Supply curve is a graphical representation of Supply schedule, express the relationship between different quantities of a commodity at different possible prices .
In the other words-Supply curve is a graphical representation of supply schedule, it shows the direct relationship between the price of a commodity and its quantity supplied during a given period of time, keeping other factor constant.
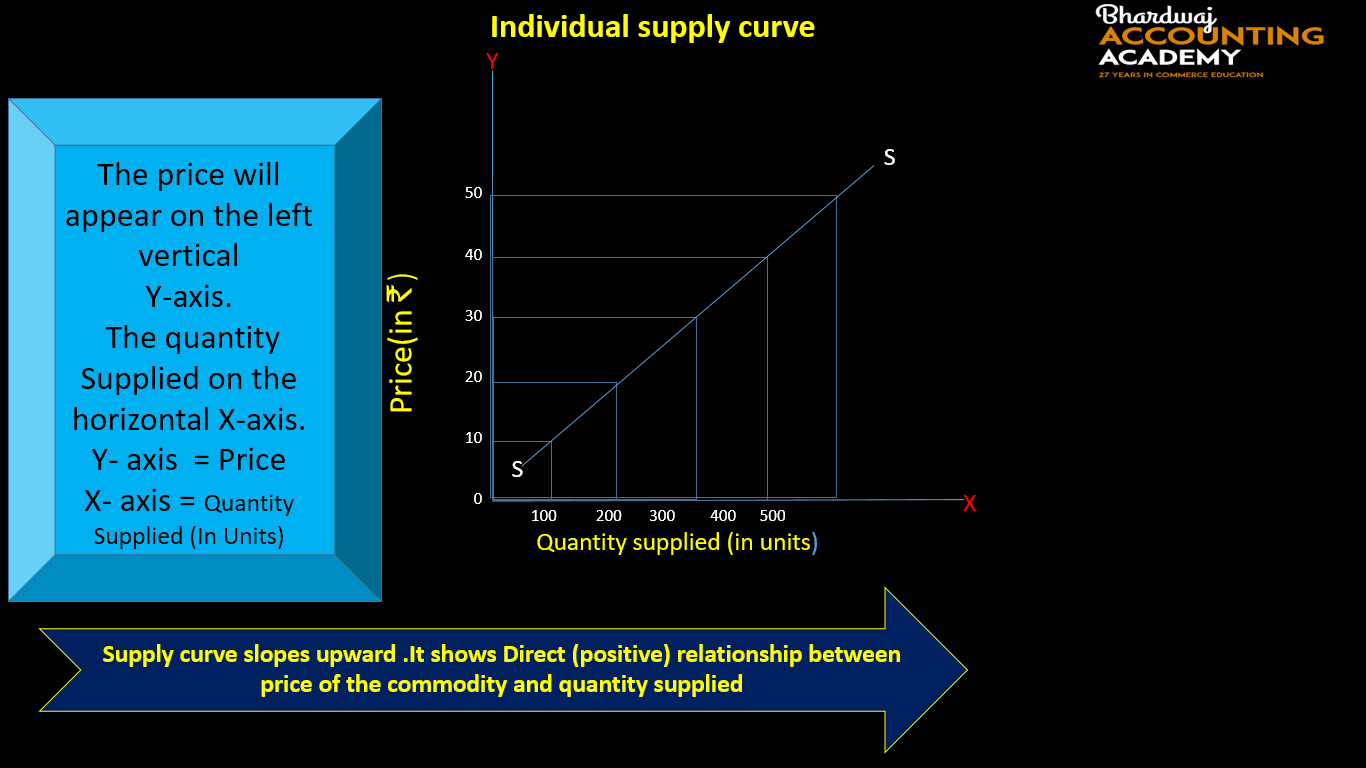
INDIVIDUAL SUPPLY CURVE
Individual supply curve refers to a graphical representation of individual supply schedule.
Or
Individual supply curve is a curve showing different quantities of a commodity that a producer is willing to offer for sale at various levels of price, during a given period of time.
INDIVIDUAL SUPPLY CURVE-
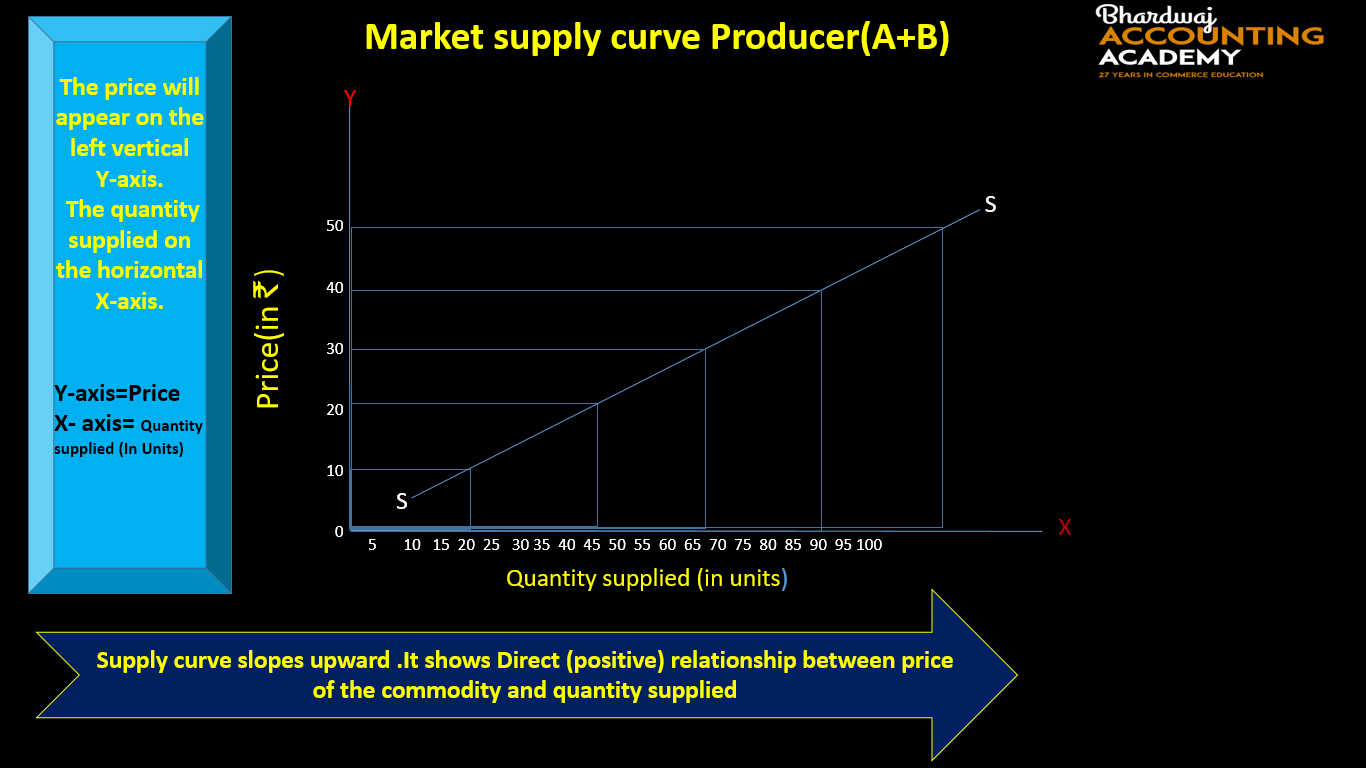
MARKET SUPPLY CURVE
Market Supply curve refers to a graphical representation of Market supply schedule.
Or
Market Demand curve is a curve showing different quantities of a commodity that all the producer are willing to offer for sale at various levels of price, during a given period of time.
MARKET SUPPLY CURVE-
SLOPE OF A SUPPLY CURVE
Slope of a supply curve is defined as the change in the variable on the y-axis divided by the change in the variable on the x-axis. It shows the Ratio between change in price corresponding to a change in quantity supplied. The slope of the supply curve equals the change in price divided by the change in quantity.
To calculate the slope of a supply curve, take two points on the curve.
Slope of a supply curve= Change in price/Change in Quantity