Table of Contents
What is Ledger?
A ledger is a book where all the transactions related to a particular account are collected at one place. Ledger is also called the Principal Book of Accounts or the books of final entry.
After recording the business transactions in the Journal or special purpose Subsidiary Books, the next step is to transfer the entries to the respective accounts in the Ledger.
A Ledger is a book which contains all the accounts whether personal, real or nominal, which are first entered in journal or special purpose subsidiary books.
Definitions of Ledger? What is Ledger?
In the words of J. R. Batliboi, “The Ledger is the chief book of accounts, and it is in this book that all the business transactions would ultimately find their place under their accounts in a duly classified form”.
In the words of L.C. Cropper,” The book which contains a classified and permanent record of all the transactions of a business is called the ledger.”
In the words of William Pickles- “The ledger is the most important book of account and i the destination of the entries made in the subsidiary books. It is essentially a collectic of the three types of accounts real, personal and nominal”.
In the words of Rolland- “Ledger is the principal book of entry”.
” The Ledger is the main or Principal book of accounts in which all the business transactions would ultimately find their place under various accounts in a duly classified form”.
Features of Ledger
- Ledger is an account book that contains various accounts to which various business transactions of a business enterprise are posted.
- It is a book of final entry because the transactions that are first entered in the journal or special purpose Books are finally posted in the ledger. It is also called the Principal Book of Accounts.
- In the ledger all types of accounts relating to assets, liabilities, capital, revenue and expenses are maintained.
- It is a permanent record of business transactions classified into relevant accounts.
- It is the Reference book of accounting system and is used to classify and summarise transactions to facilitate the preparation of financial statements.
Importance of Ledger/Utility of Ledger
Ledger is a principal or main book which contains all the accounts in which the transactions recorded in the books of original entry are transferred. Ledger is also called the ‘Book of Final Entry’ or ‘Book of Secondary Entry’,
Ledger is an important book of Account. It contains all the accounts in which all the transactions of a business enterprise are classified. The following are the advantages of ledger-
Advantages of ledger-
1.Knowledge of Business Results : Ledger provides detailed information about revenues and expenses at one place. While finding out business results the revenue and expenses are matched with each other.
2.Knowledge of Book Value of Assets : It records every asset separately. Hence, you can get the information about the Book value of any asset whenever you need.
3.Useful for Management : The information given in different ledger accounts will help the management in preparing budgets. It also helps the management in keeping the check on the performance of business it is managing.
4.Knowledge of Financial Position : It provides information about assets and liabilities of the business. From this we can judge the financial position and health of the business.
5.Instant Information : The business always need to know what it owes to others and what the others owe to it. The ledger accounts provide this information at a glance through the account receivables and payables.
6.Complete information at a glance: All the transactions pertaining to an account are collected at one place in the ledger. By looking at the balance of that account, one can understand the collective effect of all such transactions at a glance.
7.Arithmetical Accuracy: With the help of ledger balances, Trial balance can be prepared to know the arithmetical accuracy of accounts.
8. Result of Business Operations :It facilitates the preparation of final accounts for ascertaining the operating result and the financial position of the business concern.
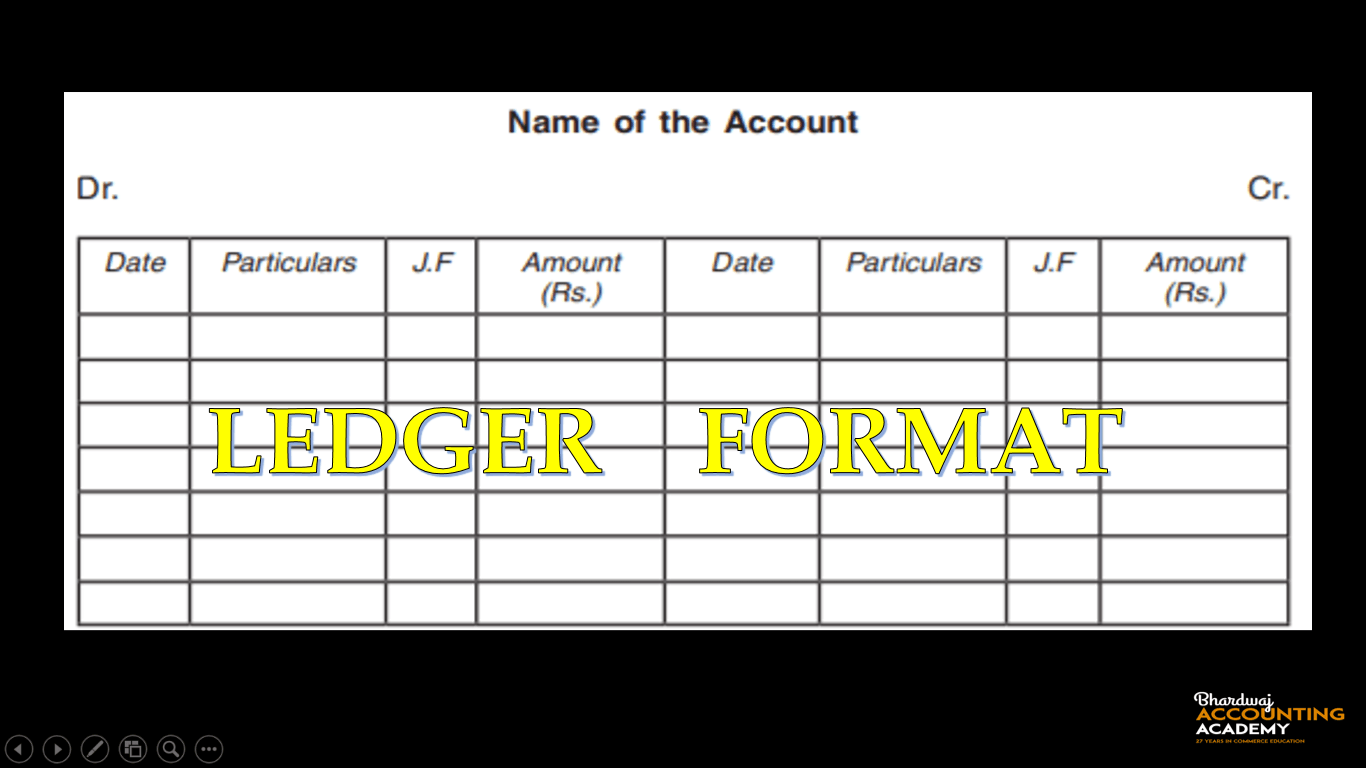
Format of Ledger
Each Ledger account is divided into two equal parts. The left-hand side is known as the debit side and the right-hand side as the credit side. As an account is in ‘T’ shape, therefore, sometimes it is called ‘T’ account. The format of an account is as shown below:-
Explanation-
(1) Each ledger account is divided into two parts. The left hand side is known as the debit side and the right hand side is known as the credit side. The words ‘Dr.’ and ‘Cr.’ are used to denote Debit and Credit.
(2) Name of the account- The name of the account is mentioned in the top (middle) of the account.
(3) Date :-The date of the transaction is recorded in this column.
(4) Particulars:-Each transaction affects two accounts. The name of the other account which is affected by the transaction is written in this column.
(5) Journal Folio or J.F. :- In this column, the page number of the Journal or Subsidiary Book from which that particular entry is transferred, is entered.
(6) Amount :-The amount pertaining to this account is entered in this column.
posting?
‘The process of transferring the entries recorded in the journal or subsidiary books to the respective accounts opened in the ledger is called Posting’
Rules of posting in Ledger-
*If an Account is debited in the journal entry, the posting in the ledger should be made on the debit side of that particular account. In the particular column the name of the other account (which has been credited in the Journal entry) should be written for reference.
* For the Account credited in the Journal entry, the posting in the ledger should be made on the credit side of that particular account . In the particular column the name of the other account (which has been debited in the Journal entry) should be written for reference.
Points to be Remember
‘To’ is written before the A/c s which appear on the debit side of ledger.
“By” is written before the A/c s appearing on the credit side.
The procedure of posting-
The procedure of posting is given as follows:
I. Procedure of posting for an Account that has been debited in the journal entry.
Step 1 Locate in the ledger, the account to be debited and enter the date of the transaction in the date column on the debit side.
Step 2 Record the name of the account credited in the Journal in the particulars column on the debit side as “To….. (name of the account credited)”.
Step 3 Record the page number of the Journal in the J.F column on the debit side and in the Journal, write the page number of the ledger on which a particular account appears in the L.F. column.
Step 4 Enter the relevant amount in the amount column on the debit side.
II. Procedure of posting for an Account that has been credited in the journal entry.
Step 1 Locate in the ledger the account to be credited and enter the date of the transaction in the date column on the credit side.
Step 2 Record the name of the account debited in the Journal in the particulars column on the credit side as “By…… (name of the account debited)”
Step 3 Record the page number of the Journal in the J.F column on the credit side and in the Journal, write the page number of the ledger on which a particular account appears in the L.F. column.
Step 4 Enter the relevant amount in the amount column on the credit side
” Use of these words ‘To’ and ‘By’ is optional “.