Table of Contents
Discount Received Journal Entry
Discount?
The concession given by the seller to his customer in the price of the goods is called a discount.
In other words, a discount is a rebate given by the seller to the buyer. There are mainly two types of discount- 1. Trade Discount 2. Cash Discount
1. Trade Discount-
The reduction in the list price with the aim of motivating the customers to buy more goods is called a trade discount. This discount is given on both cash and credit transactions, it is not recorded in the books of account, it is shown by deducting it directly in the invoice.
2. Cash Discount-
The discount allowed to the customers for the purpose of making quick payments is called a cash discount, this discount is given only on cash deals. This discount is given on the amount paid. This is recorded in the books of account.
We received a discount when we make timely payments to a creditor. When a discount is received, an entry is made in the journal as follows:
Discount received journal entry (According to Traditional Approach)
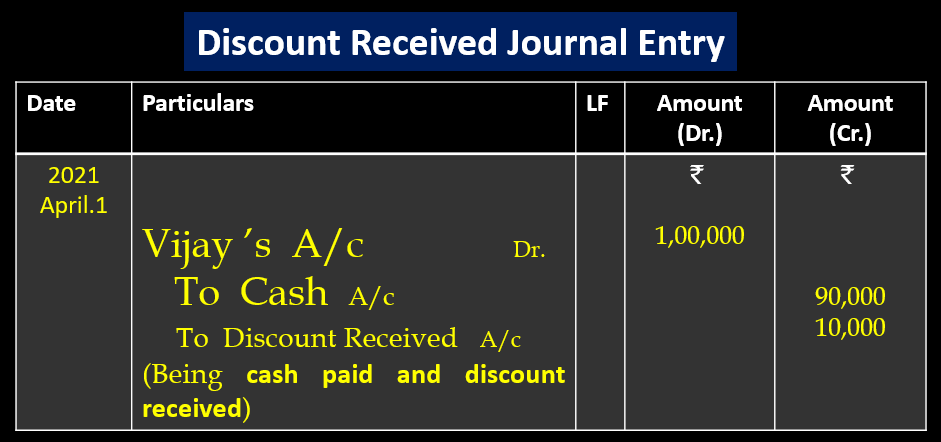
Example- Vijay has to pay ₹1,00,000. In full settlement ₹ 90,000 was paid and a discount received ₹10,000.
Explanation: According to the traditional approach in this transaction, Three accounts are affected-
1. Vijay’s account (Personal Account)
Rules of Personal Account– Debit the receiver, credit the giver. Here Vijay is the receiver of cash, so according to the rules (Debit the receiver), Vijay’s account will be debited ₹1,00,000 while passing the journal entry.
2. Cash account (Real Account)
Rules of Real Account– Debit what comes in, Credit what goes out. Here cash is going out from the business, so according to the rules, the Cash account will be credited ₹90,000 while passing the journal entry.
3. Discount Received account (Nominal Account)
Rules of Nominal Account: Debit all losses and expenses, and credit all Income and gain.
Discount Received Account will be credited ₹10,000 as per the rules (credit all Income and gain) at the time of passing the journal entry.
Discount Received Journal Entry (Traditional Approach)
Discount received journal entry (According to Modern Approach)
Example- Vijay has to pay ₹1,00,000. In full settlement ₹ 90,000 was paid and a discount received ₹10,000.
Explanation: According to the Modern approach in this transaction, Three accounts are affected-
1. Vijay’s account (Creditors) (Liabilities Account)
Rules of liabilities Account– Increases in liabilities are credits; decreases in liabilities are debits. Here liabilities decrease in the form of creditors, so according to the rules (decreases in liabilities are debits), Vijay’s account will be debited ₹1,00,000 while passing the journal entry.
2. Cash account (Assets Account)
Rules of Assets Account– Increases in assets are debits; decreases in assets are credits.
Here the assets decrease in the form of cash, according to the rules,(decreases in assets are credits) cash account will be credited ₹90,000 while passing the journal entry.
3. Discount Received account (Revenue Account)
Rules Revenue Account: Increases in incomes and gains are credits; decreases in incomes and gains are debits.
The revenue is increasing in the form of Discount received here, so the Discount received account will be credited ₹10,000 as per rules(Increases in incomes and gains are credits) while passing the journal entry.
Discount Received Journal Entry (Modern Approach)

Commission received journal entry
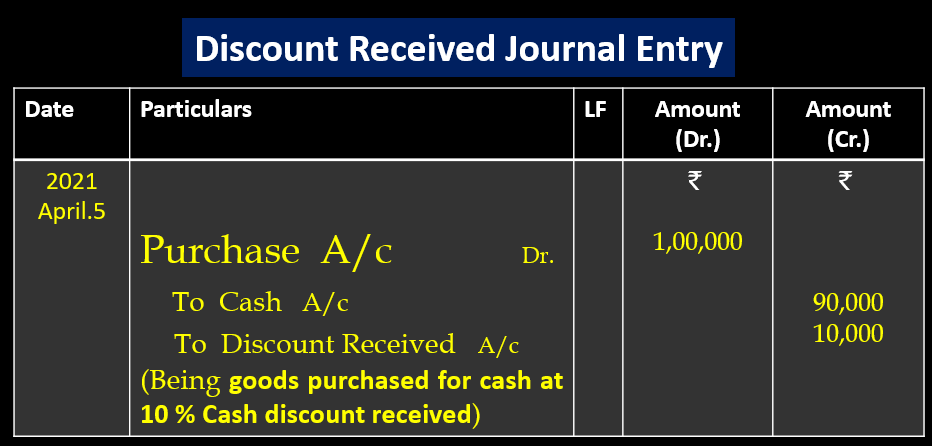
Example- April 1, 2021 Bought goods for cash of the list price ₹1,00,000 at 10% cash discount. Pass journal entry.
Solution-
List Price =₹1,00,000
Cash Discount= @10% on ₹1,00,000
Cash Discount Received = ₹10,000
Net Amount paid= ₹1,00,000- ₹10,000
= 90,000
Discount Received Journal Entry
Discount Received Journal Entry