Table of Contents
Introduction to Petty Cash Book
In every business, of whatever size, there are many small cash payments such as conveyance, cartage, carriage, postage, telegram, printing, and stationery, refreshments. coolie charges, etc. These expenses are generally repetitive. If all these small payments are recorded in the cash book, it will be difficult for the cashier to maintain the records all by himself.
To simplify the Cashier’s task, these small and recurring expenses are recorded in a separate cash book called “Petty Cash Book” and the person who maintains the petty cash is called the “Petty Cashier”.
In other words
” petty cashier makes payments of these expenses and maintains a separate cash book to record these transactions. Such a cash book is called Petty Cash Book”.
Petty means ‘small’. The petty cash book is a book where small recurring payments like carriage, cartage, postage and telegram, printing and stationery etc., are recorded by the petty cashier, a person other than the main cashier.
Process of petty cash book-
The petty cashier works on the imprest system. Imprest means ‘money advanced on loan’
Under this system, a definite sum, say $ 5000 is given to the petty cashier at the beginning of the period. This amount is called imprest money. The petty cashier meets all small payments out of this imprest amount, At the end of the period say one month he presents the account to the Head Cashier and gets reimbursed from the Head Cashier.
Suppose out of $ 5,000 he has spent $ 3,800 by the end of the month. He will get $3,800 from the head cashier. Thus, again he has the full imprest amount at the beginning of the next period. The reimbursement process can be weekly, fortnightly or monthly depending upon the frequency of small payments.
Thus the system of reimbursing the amount spent by the petty cashier at a fixed period is known as the imprest system of petty cash.
The Petty Cashier is authorized to sanction and disburse small payments. Assignment of the task of making of petty expenses to a person and the maintenance of petty cash book by him reduces the burden of the Head Cashier.
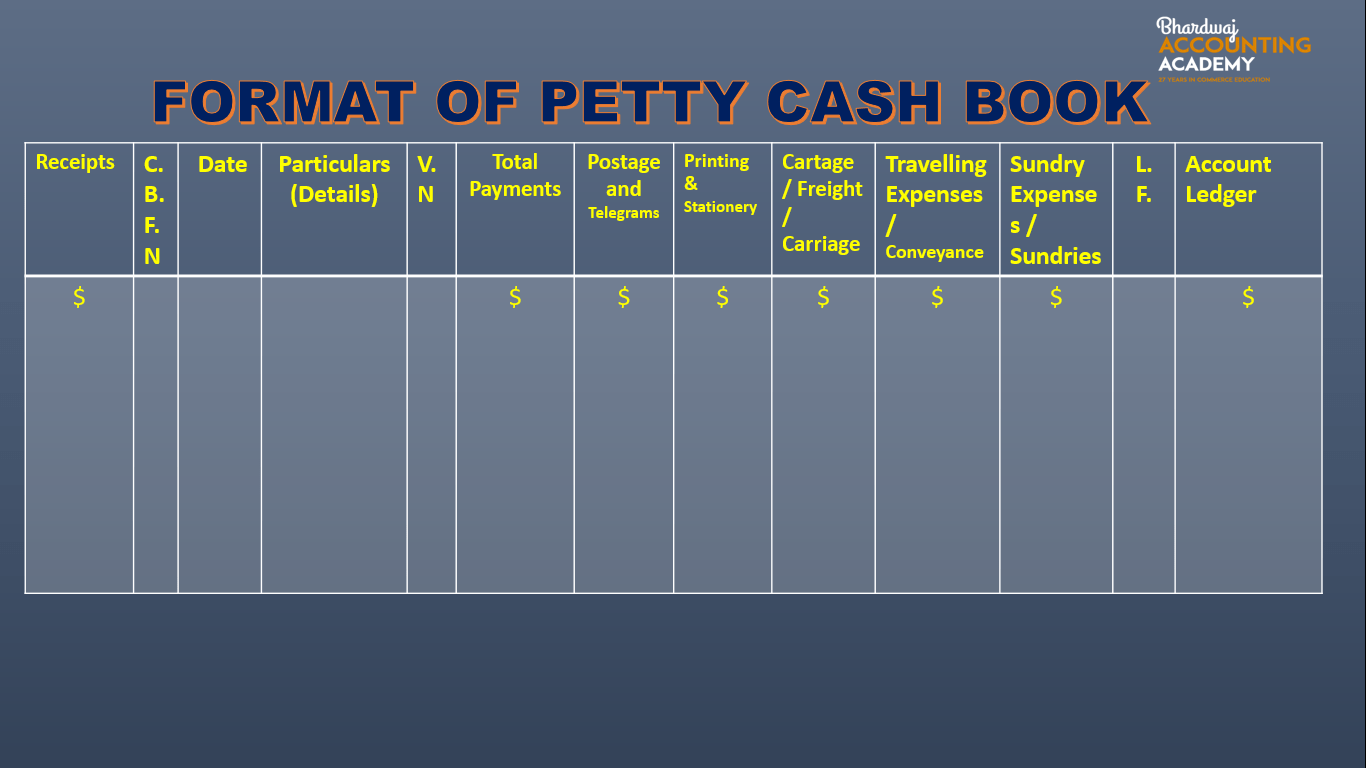
Format of Petty cash book-
Explanation of columns in the analytical petty cash book
1. Receipts: This is the first column of the petty cash book. Amount received by the petty cashier for meeting petty
expenses and the opening balance of petty cash will be recorded in this column.
2. C.B.F.N: This refers to Cash Book Folio Number. In this column we write the page number of the cash book where cash paid by the cashier is recorded.
3. Date: In this column, the date of receipt / payment of cash is recorded.
4. Particulars: This column records the details of the receipts / payments. Cash received in the beginning is shown as ‘To cash’ and all the petty expenses are shown as ‘By expenses’ (name of the expense).
5. V.N.: The serial number of the voucher (cash payment) is written in this column.
6. Total Payments: This column records the amount of every expense. At the end of the week or month expenses are totalled and afterwards balanced. The total expenses of the week or the month is compared with the total of the receipts column and the balance is obtained.
7. Postage and Telegrams: This column records postal expenses like post card, envelope, inland letter, postage stamps, registered letter, parcel, telegrams and telephone charges.
8. Printing & Stationery: It includes expenses incurred for purchasing materials such as paper, ink, pencil, eraser, carbon paper and other items of stationery.
9. Cartage / Freight / Carriage: In this column carriage inward of goods is recorded. It includes cartage paid to coolie, tempo charges etc.
10. Travelling Expenses / Conveyance: In this column fare for hiring autorickshaw, bus, train, taxi etc., are recorded.
11. Office Expenses & Repairs: Minor repairing charges and petty office expenses like cleaning are included in this column.
12. Sundry Expenses / Sundries: Generally columns of important petty expenses of the business according to the nature and type of business are prepared. In addition to these important expenses, there may be certain expenses, which may not have specific columns for them.
Expenses like refreshment, charity, tips, amount paid to scavangers etc., are recorded in this column.
13. L.F.: This refers to the page number of the ledger where the respective account is recorded.
14. Personal Accounts : Small amount of money paid to individuals are entered in this column.
Balancing Of Petty Cash Book –
At the end of the period i.e., week or month the total payments column and individual expenses columns are totalled. It should be ascertained that the total of petty expenses column must be equal to the total of payments column.
The total payments column is compared with the total of receipts column and balance is obtained. The closing balances is shown as ‘By Balance c/d’.
The closing balance is carried forward to the beginning of the next week or month. It is shown as ‘To Balance b/d’.
Advantages of analytical Petty Cash Book-
1. Very Simple Method of recording petty expenses: It is a very simple method of recording petty expenses. The maintenance of petty cash books does not require specialized knowledge of accounting.
2. Economy of Time: It requires less time to record and also saves the time of the head cashier.
3. Lesser chances of mistakes: The petty cash book is checked by the head cashier at the end of the specified period. This process minimizes the chances of mistakes.
4. Frauds can be minimized: Recording transactions on the basis of vouchers and checking of cash book by the main cashier minimizes the chances of fraud.
5. Control of petty expenses.
6. Saving time and effort of Head cashier.
Question 1.
Prepare Petty Cash Book on imprest system from the following particulars.
2021
September. 1. Received for petty cash payments $1,000
September. 4. Paid for stationery $140
September. 9. Paid for postage $60
September. 10. Paid for printing charges $150
September. 11. Paid for carriage $125
September. 17. Paid for telegrams $25
September. 20. Purchased envelops $30
September. 21. Paid for coffee to office staff $30
September. 22. Paid for office cleaning $50
September. 28. Paid for cartage $100
September. 30. Paid to Robert $50
Solution 1.
PETTY CASH BOOK
Question 2.(For Practice)
Prepare Petty Cash Book on imprest system from the following particulars.
2021
September. 1. Received for petty cash payments $5000
September. 4. Paid for stationery $240
September. 9. Paid for postage $125
September. 10. Paid for printing charges $250
September. 11. Paid for carriage $225
September. 17. Paid for telegrams $425
September. 20. Purchased envelops $430
September. 21. Paid for coffee to office staff $230
September. 22. Paid for office cleaning $350
September. 28. Paid for cartage $100
September. 30. Paid to Robert $350
Also read: Financial Accounting Quiz Questions and Answers
Also read : Classified Balance Sheet
Also read : Fictitious Assets