Table of Contents
30 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger, Trial balance, and Final Accounts- Project
30 transactions For accounts Project
Pass The Journal entries, which Should Have At Least 30 Transactions (Without GST), and post them into the ledger. Closing The Books Of Accounts Prepare A Trial Balance And Final Accounts (trading and profit and loss accounts, Balance sheet):
Want to make 20 transaction project check out this link: 20 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger and Trial balance
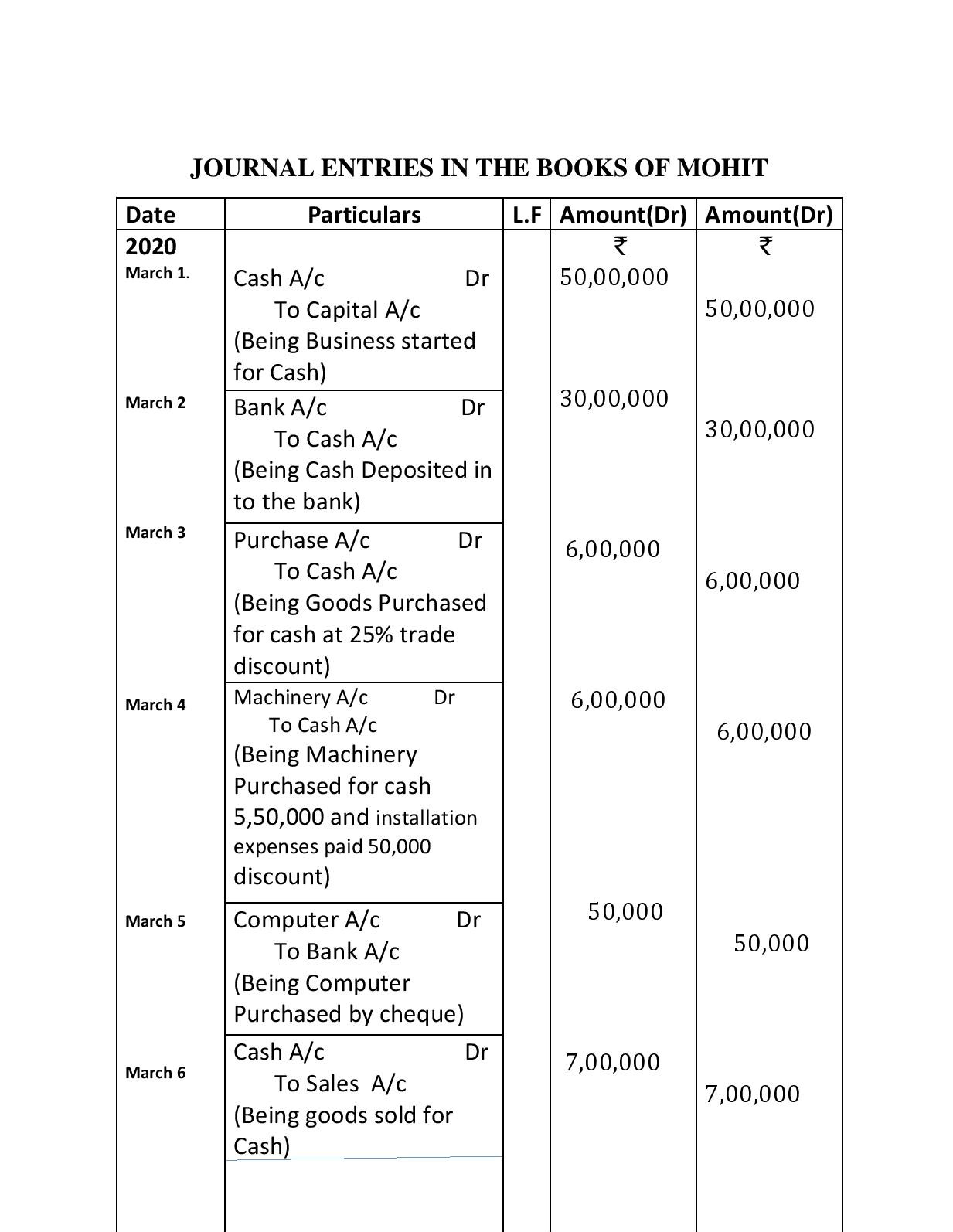
On March 1, 2020, Mr. Mohit started a Furniture business in GANDHI NAGAR Mr. Mohit invested Rs 50,00,000.
March 2: Cash deposited into the bank: Rs. 30,00,000.
March 3: Goods purchased (3,000 chairs) for cash: Rs 8,00,000 at a 25% trade discount.
March 4: Machinery was purchased for cash of Rs. 5,50,000, and installation expenses of Rs. 50,000 were paid.
March 5: Computer Purchased paid by cheque for Rs. 50,000.
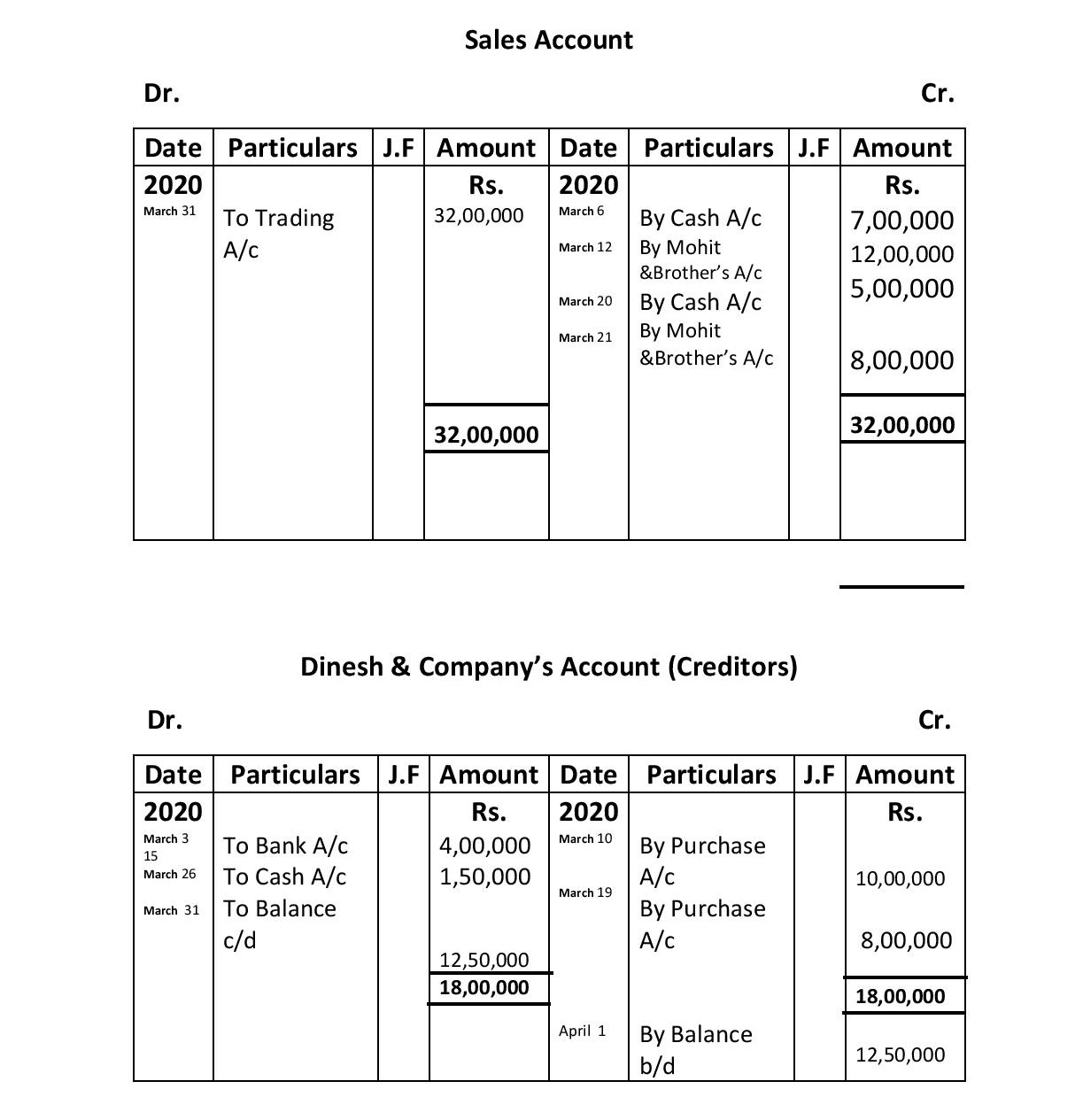
March 6: Goods sold (2,000 chairs) for cash: Rs. 7,00,000.
March 7: Carriage paid Rs. 18,000.
March 10: Goods purchased (1,000 tables) from Dinesh & Company: Rs. 12,50,000 at a 20% trade discount.
March 12: Goods Sold( 500 Tables) to Mohit & Brother: Rs. 20,00,000 at 40% trade discount.
March 13: Investment purchased by check for Rs. 2,00,000.
March 15: The amount paid to Dinesh & Company by cheques was Rs. 4,00,000.
March 16: Furniture Purchased for office use and paid by cheque for Rs. 1,50,000.
March 17: Cash withdrawn for personal use: Rs. 40,000.
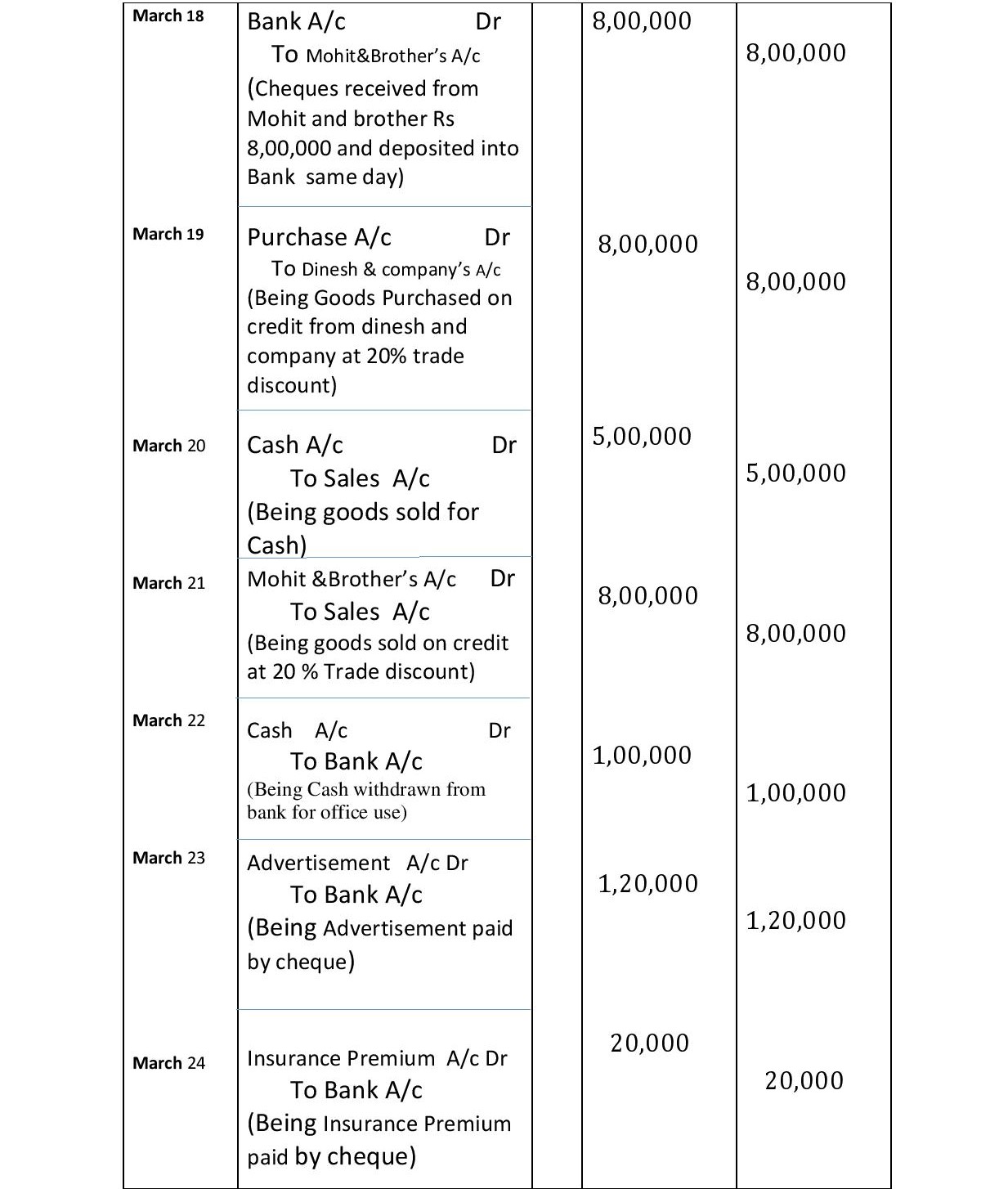
March 18 Cheques received from Mohit and brother Rs 8,00,000 were deposited into the bank on the same day.
March 19 Goods purchased ( 1000 Tables) from Dinesh & company Rs. 10,00,000 at 20% trade discount.
March 20: Goods sold for cash, Rs. 5,00,000.
March 21 Goods Sold ( 500 Chairs and 500 tables) to Mohit & Brother Rs.10,00,000 at 20% trade discount.
March 22 Cash withdrawn from bank for office use Rs. 1,00,000.
March 23 Advertisement Expenses paid by cheque Rs. 1,20,000.
March 24 Insurance premium paid Rs. 20,000 by cheque.
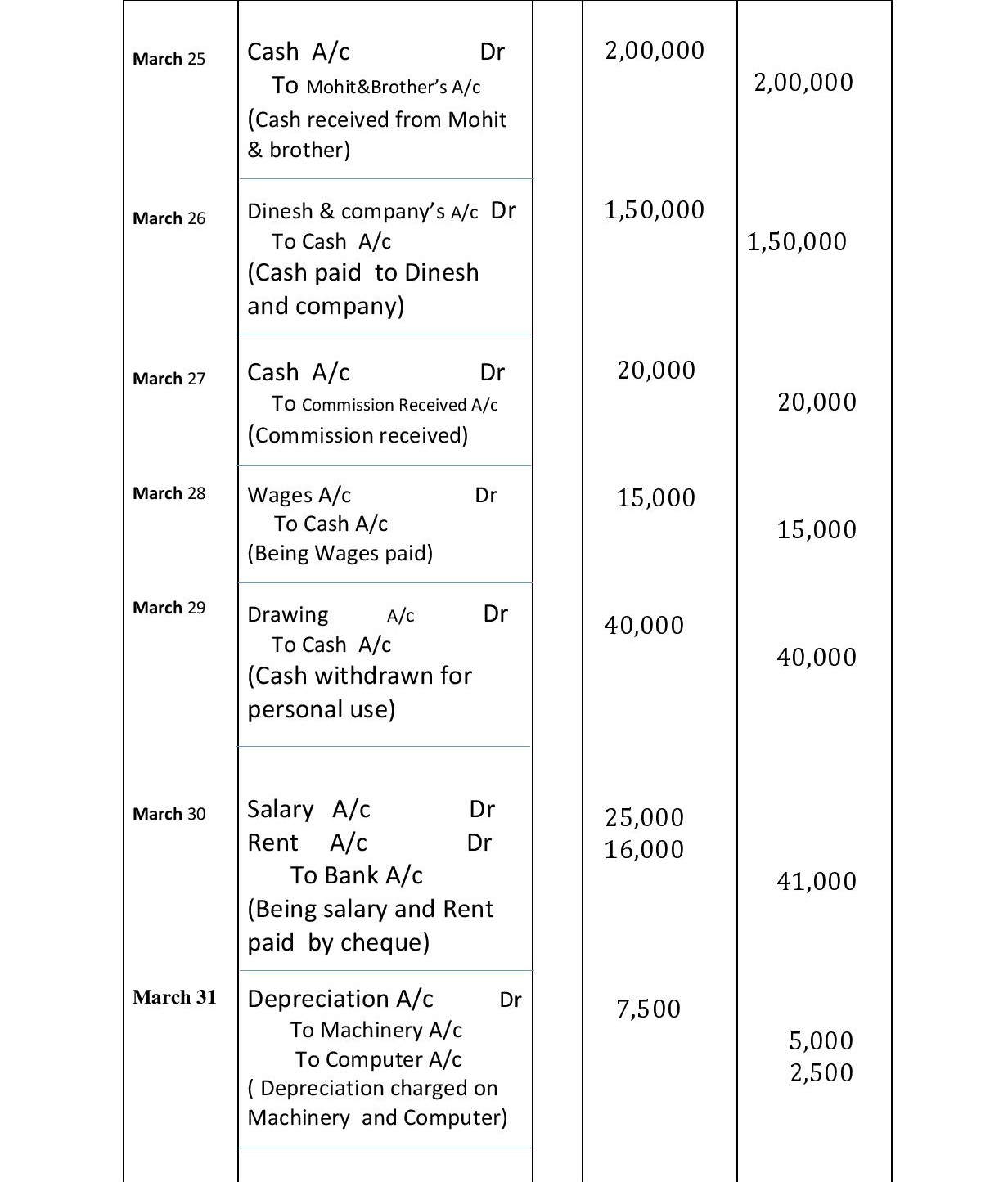
March 25 Cash received from Mohit & brother Rs 2,00,000.
March 26: Cash paid to Dinesh & Company: Rs. 1,50,000.
March 27, the Commission received Rs. 20,000.
March 28: Wages paid: Rs. Rs.15,000.
March 29 Cash withdrawn for personal use Rs. 40,000.
March 30 Salary Rs 25,000, Rent Rs. 16,000 paid by cheque.
March 31 Depreciation charge on machinery Rs. 5,000.
March 31 Depreciation charge on Computer Rs. 2,500.
March 31 Bank charges charged by bank Rs. 5,000.
March 31. Interest received on the investment Rs. 4,000.
These are the 30 transactions which happened in the business in the month of March 2020
Also read : Golden Rules Of Accounting
30 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger, Trial balance, and Final Accounts- Project
Know about Admission of a new partner MCQs with Solved answer 12 cbse
30 transactions Journal Entries
30 transactions Ledger Accounts
Understand the Concept of Goodwill
Balancing of different accounts in 30 Transactions
Balancing is done periodically, i.e., weekly, monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly, depending on the requirements of the business.
- Personal Accounts : These accounts are generally balanced regularly to know the amounts due to the persons (creditors) or due from the persons (debtors).
- Real Accounts : These accounts are generally balanced at the end of the financial year, when final accounts are being prepared. However, a cash account is frequently balanced to know the cash on hand. A debit balance in an asset account indicates the value of the asset owned by the business. Asset accounts always show debit balances.
- Nominal Accounts : These accounts are, in fact, not to be balanced as they are to be closed by transfer to final accounts. A debit balance in a nominal account indicates that it is an expense or loss. A credit balance in a nominal account indicates that it is an income or gain.
All such balances in personal and real accounts are shown in the Balance Sheet, and the balances in nominal accounts are taken to the Trading and Profit and Loss Account.
- Balance of Direct expenses Accounts are transferred to the debit side of the trading account.
- The balance of the purchase account is transferred to the debit side of the trading account.
- Balances of direct income (sales) accounts are transferred to the credit side of the trading account.
- Balance of Indirect expenses Accounts are transferred to the debit side of the profit and loss account.
- Balances of indirect income accounts are transferred to the credit side of the profit and loss account.
How to make trial balance: Trial Balance Definition and methods

Financial statements and final accounts for 30 Transactions
The statements that are prepared at the end of a particular accounting period to measure the overall result (net profit or net loss) of business activities and show the financial position of a business concern are generally called financial statements.
Or
The accounts that are prepared at the final stage (at the end of the financial year) of the accounting cycle to know the profit or loss and financial position of a business concern are called final accounts.
Final accounts give an idea of the profitability and financial position of a business to its management, owners, and other interested parties.
Financial statements and final accounts include these statements :
(i) Income statement (a. Trading Account, b. Profit and Loss Account)—prepared to ascertain gross profit/loss and net profit/loss during an accounting period.
A trading account is prepared to ascertain the results of the trading activities of the business enterprise. Trading activities mean the buying and selling of goods. The trading account shows the result (gross profit/gross loss) of buying and selling goods.
The profit and loss account shows the net profit/loss during an accounting period. A profit and loss account is an account, that is prepared to calculate the net profit or net loss of the business for the accounting period. The profit and loss account is a nominal account, and as such, all the indirect expenses and losses are shown on the debit side and all the incomes and gains are shown on the credit side.
Check the Format of Trading Account
Learn about the format of Profit And Loss Account
(ii) Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)—prepared to ascertain Financial position (assets, liabilities and capital) of an enterprise at a particular point of time. Balance sheet is a financial statement that shows the financial position of a business and the nature and values of its assets and liabilities on a particular date.
- This forms the second part of the final accounts.
- It is a statement showing the financial position of a business.
- Balance sheet is prepared by taking up all personal accounts and real accounts (assets and properties) together with the net result obtained from profit and loss account.
- On the left hand side of the statement, the liabilities and capital are shown.
- On the right hand side, all the assets are shown.
- Balance sheet is not an account but it is a statement prepared from the ledger balances. So we should not prefix the accounts with the words ‘To’ and ‘By’.
Balance sheet is defined as ‘a statement which sets out the assets and liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date’.(particular point of time).
Direct Expenses
Those expenses which are incurred on purchasing of goods and for converting raw material into the finished goods .
Or
Those expenses which are directly related to production/Manufacturing of goods or purchase of the goods are called direct expenses.
For example, Manufacturing wages, Expenses on purchases (including all duty and tax paid on purchases), Brokerage on purchases of goods, Commission on purchases of goods), Carriage/Freight/Cartage inwards, Production expenses (such as power and fuel, water, coal, gas, etc.), factory expenses (e.g. lighting, rent and rates), Royalty based on production, etc.
Note : All direct expenses are debited to the trading account.
Direct Income
Direct income is the income that is directly related to the particular business, e.g., sales of goods.
In other words, direct income is one that is earned directly by way of business activities.
Note : All direct income are credited to Trading account.
Indirect Expenses
Those expenses which are not directly related to production/Manufacturing or purchase of the goods are called indirect expenses. It includes those expenses which are related to office and administration, selling and distribution of goods and financial expenses etc.
For example, Office & administrative expenses, Salaries, and Rates Taxes, Printing and Stationery, Salaries & Wages, Postages and Telephones , Office Lighting, Insurance Premium, Legal Expenses, Audit Fees, Travelling Expenses , Selling & Distribution Exp. Carriage and Freight Outwards, Commission , Brokerage, Advertisement , Publicity Bad Debts Packing Expenses Salaries of Salesmen Delivery Van Expenses, Financial Exp. Interest paid on loans, Discounts Allowed Rebate Allowed Bank Charges Miscellaneous Exp. Repairs Depreciation on Fixed Assets Entertainment Expenses, Donations, and Charity, Stable Expenses Unproductive Expenses
Note: :These expenses are shown in the debit side of the profit and loss account.
Indirect Income.
Indirect income is one that is earned directly by way of non-business activities. e.g., profit on sale of fixed assets, profit on sale of investment, discount received, rent received, commission received, interest received, dividend received, etc.
Note : All Indirect income are credited to Profit and loss account
Operating Expenses
An operating expense is a day-to-day expense incurred in the normal course of business. These expenses appear on the income statement.
Or
Operating expenses are the expenses that are incurred by the business in the normal course of its operations.
Or
Operating expenses are expenses a business incurs in order to keep it running, such as employee benefit expenses, Depreciation and amortization Expenses , Selling and distribution expenses, Rent and administrative expenses, rent tax and insurance, etc.
Non- Operating Expenses
Such expenses that are neither related to the normal course of activities of a business nor related to the production process of a business are known as non-operating expenses.
Non-Operating Expenses = Interest on Debentures / Long Term Loans + Loss on sale of Non-Current Assets
Non-Operating Incomes
Non-operating income is the portion of an organization’s income derived from activities unrelated to its core business operations.
Non Operating Incomes = Interest Received on Investment + Profit on sale of Non-Current Assets+ Dividend received













Nice information
Nice Problem
can anyone pls help me by sending me a double column cash book. at my insta – @bhavya_.26 , or twitter- @bhavya7419
I want to know double column cash book
Read:
https://jkbhardwaj.com/double-column-cash-book-cash-and-bank/
https://jkbhardwaj.com/double-column-cash-book-cash-and-bank/
Could you show how you calculated closing stock for this situation in a more detailed manner!?
Closing Stock is calculated as follows:
The unsold stock of chairs: Chairs purchased 3000 @200 each- Chairs sold (2000+500)= Unsold chairs 500×200= 1,00,000
The uosold stock of Table : Table purchased 1000 @1000 each + 1000 @800 each – Table sold (500+500)= unsold table 1000×800= 8,00,000 (FIFO METHOD)
Total Stock At the end of the financial year= Chairs1,00,000+ Table8,00,000= 9,00,000(closing stock)
After the 2nd time of purchase of an item what will be the new price of the item…so we get the closing stock at mentioned amount (900000)
Closing Stock is calculated as follows:
The unsold stock of chairs: Chairs purchased 3000 @200 each- Chairs sold (2000+500)= Unsold chairs 500×200= 1,00,000
The uosold stock of Table : Table purchased 1000 @1000 each + 1000 @800 each – Table sold (500+500)= unsold table 1000×800= 8,00,000 (FIFO METHOD)
Total Stock At the end of the financial year= Chairs1,00,000+ Table8,00,000= 9,00,000(closing stock)
This content is helpful for me in learning the concepts of the journal, ledger and trial balance with examples & solve practical problems. This was really helpful to gain knowledge as well. Thanks to jkbhardwaj
It is really really helpfull for me sir,
THANKYOU FOR GIVING US SUCH A GREAT INFORMATION BY YOUR HARDWORK🙏
Thank you soo much Sir for this wonderful information. This is very helpful as I had to made a assignment on this Topic so I was little bit confused butt as I found this I get all the things very well. So, once again thanks a lot Sir that you do so much hardwork for us so that we can study well & understand the things easily.🙏🙏
Thank you so much sir
Thank you so much sir for giving us such a great information🙂..
Nice website
Helpful for me to study
Nice website
This website is helpful for doing my project.
Thank you sir,for giving us such a great information
very informative article for beginners
i realy like it very easy and understand able material