Table of Contents
What is Trial Balance? Format definition and methods.
Trial balance Meaning?
Trial balance Meaning: It is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of ledger accounts.
Trial Balance is the list of debit and credit balances taken out from ledger to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books. “It also includes the balances of Cash and bank taken from the Cash Book”. Trial Balance format is also shown in this article.
First step recording of transactions in a journal. The next step post them into the ledger and the next step in the accounting process is to prepare a statement to check the arithmetical accuracy of the transactions recorded so for. This statement is called ‘Trial Balance’.
Trial balance is a statement that shows debit balances and credit balances of all accounts in the ledger. Since every debit should have a corresponding credit as per the rules of the double-entry system, the total of the debit balances and credit balances should tally (agree). In case, there is a difference, one has to check the correctness of the balances brought forward from the respective accounts. Trial balance can be prepared on any date provided accounts are balanced.
Definition
“Trial balance is a statement, prepared with the debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books” – J.R. Batliboi.
A trial balance is a statement that shows the balances of all ledger accounts (debit or credit) on a particular date, to verify the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
Also Read: 20 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger, and Trial balance
Features of Trial Balance
-
List of Balances – A Trial Balance is a list of debit and credit balances of various ledger accounts.
-
Form of Statement – It is prepared in the form of a statement, not an account.
-
Check of Arithmetical Accuracy – It is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts.
-
Limited Accuracy – Agreement of the trial balance is not conclusive proof of correctness; some errors may still remain undetected.
-
Periodicity – It is usually prepared at the end of the accounting year, but can also be prepared weekly, monthly, quarterly, or half-yearly.
-
Not a Part of Final Accounts – Trial Balance is not a part of the final accounts, but a preliminary step.
-
Summary of Ledger Accounts – It provides a concise summary of all ledger accounts.
-
Link – It serves as a connecting link between the books of accounts and the final accounts (Trading A/c, Profit & Loss A/c, and Balance Sheet).
-
Basis for Financial Statements – It facilitates the preparation of financial statements by providing all ledger balances in one place.
Objectives of Trial Balance
-
To check arithmetical accuracy – It helps to check whether the debit and credit balances of ledger accounts are recorded correctly.
-
To detect errors – It helps in locating certain types of errors like wrong balancing or posting.
-
To provide a summary – It gives a summary of all ledger accounts at one place.
-
To prepare final accounts – It acts as the basis for preparing Trading A/c, Profit & Loss A/c, and Balance Sheet.
-
To save time and effort – By listing all balances together, it makes the preparation of accounts quicker and easier.
Advantages
- Trial balance helps to ascertain the arithmetical accuracy of the book-keeping work done during the period.
- It supplies in one place ready reference of all the balances of the ledger accounts.
- If any error is found out by preparing a trial balance, the same can be rectified before preparing final accounts.
- It is the basis on which final accounts are prepared.
Limitations 0f trial balance
Though the trial balance helps to ensure the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts, it is possible only when the accountant has not committed any errors. As not all the errors made are disclosed by the trial balance, it would not be regarded as conclusive proof of the correctness of the books of accounts maintained.
Errors don’t Affect the Trial Balance
(1) Errors of complete commission.
(2) Wrong recording in the books of original entry.
(3) Complete omission from posting.
(4) Errors of posting to the wrong Account but on the correct side.
(5) Compensating errors.
(6) Errors of principles.
Errors Affecting Trial Balance
- Error in totaling of subsidiary books as undercast or overcast.
- Error in the balancing of ledger accounts.
- Error in posting to the correct Account, but the wrong amount.
- The error of partial omission.
Also Read: Meaning and advantages of Double Entry System
Methods Of Trial Balance –A trial balance can be prepared in the following methods-
The Total Method or Gross Trial Balance Method :
This is a very simple method of preparing a trial balance. According to this method, the total amount of the debit side of the ledger accounts are shown on the debit side of the Trial Balance and the total amount of the credit side of the ledger accounts are shown on the credit side of the Trial Balance. After this, the debit and credit column of the trial balance is totaled. If they are equal it is assumed that there is no arithmetical error in the posting of Ledger Accounts.
EXAMPLE 1. Trial Balance format
TRIAL BALANCE FORMAT
(Total Method)
As on 31st March, 2020
| Name Of Accounts | L.F. | Debit Total
(Amount) |
Credit Total
(Amount) |
|
Cash Account Machinery Account Building Account Capital Account Purchase Account Sales Account Goodwill Account Purchase Return Account Sales Return Account Depreciation Account Wages Account Salaries Account Selling and distribution Account Carriage inward Account Drawing Account Repairs Account Rent Account General Reserve Account Debtors Account Creditors Account Bank Account
|
8,50,000 10,00,000 15,00,000 ………… 16,00,000 ………… 1,00,000 …………. 50,000 1,00,000 20,000 50,000 1,25,000 25,000 50,000 12,000 18,000 ………… 5,20,000 80,000 4,75,000
|
3,50,000 2,00,000 ……….. 20,10,000 30,000 26,00,000 ………… 75,000 ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… 3,00,000 1,20,000 4,80,000 4,10,000
|
|
| TOTAL | 65,75,000 | 65,75,000 |
trial balance format
The Balance Method Net trial balance Method :
In this method, only the balances of an account, either debit or credit, as the case may be, are recorded against their respective accounts. The balance method is more widely used, as it supplies ready figures for preparing the final accounts.
Also Read: Bank Reconciliation Statement
preparation: Steps (Only Balance Method)
- Date on which the trial balance is prepared should be mentioned at the top.
- Name of the Account column contains the list of all ledger accounts.
- Ledger folio of the respective account is entered in the next column.
- Ledger Accounts which shows a debit balance is put on the Debit side of the trial balance.
- Ledger Accounts that Showing credit balance is put on the Credit side of the Trial Balance.
- Accounts which show no balance i.e. whose Debit and Credit totals are equal are not entered in Trial Balance.
- There is always debit balance of the purchase account, sales return account and opening stock account.
- There is always a credit balance for the sales account, purchase return account etc.
- All assets such as cash, Machine, furniture, building, Goodwill, Bills receivable, Debtors, prepaid expenses, Fixtures and fittings, Motor Vehicles, bank, Computer, Accrued income, etc. are always debit balance.
- All Liabilities such as capital, creditors, Bills Payable, Outstanding expenses, loans, mortgage loans, bank overdraft, advance income etc. are always have credit balance.
- All expenses and losses such as wages, salaries, Trade expenses, general expenses, interest paid, commission paid, discount allowed, rent paid, interest on capital, interest on loan, Depreciation, Bad Debts and all types of direct and indirect expenses are always have debit balance.
- All types of income such as rent received, interest received, commission received, discount received, interest on Investment, Dividend Received etc. are always have credit balance.
- There is always credit balance of accounts like capital reserve, general reserve, Investment fluctuation Reserve, Tax Reserve, Capital Redemption reserve, Debenture redemption reserve, securities Premium Reserve, etc.
- Then the two sides of the Trial Balance are totalled. If they are equal, it is assumed that there is no arithmetical error in the posting and balancing of Ledger Accounts.
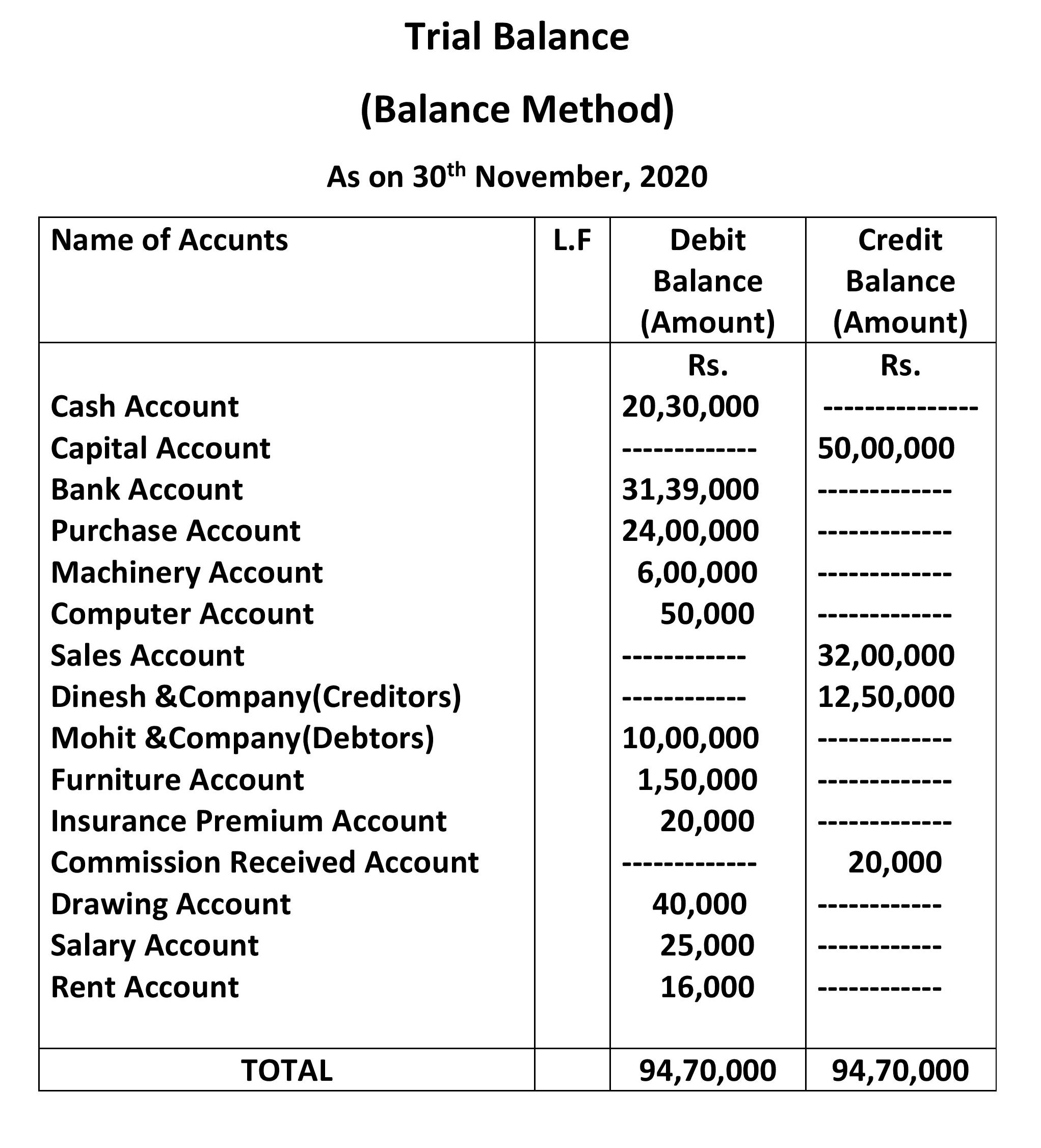
EXAMPLE 2. Trial Balance format
TRIAL BALANCE FORMAT
(Balance Method)
As on 31st March, 2020
| Name Of Accounts | L.F. | Debit Balance
(Amount) |
Credit Balance
(Amount) |
|
Cash Account Machinery Account Building Account Capital Account Purchase Account Sales Account Goodwill Account Purchase Return Account Sales Return Account Depreciation Account Wages Account Salaries Account Selling and distribution Account Carriage inward Account Drawing Account Repairs Account Rent Account General Reserve Account Debtors Account Creditors Account Bank Account
|
5,00,000 8,00,000 15,00,000 …………. 15,70,000 …………. 1,00,000 ………… 50,000 1,00,000 20,000 50,000 1,25,000 25,000 50,000 12,000 18,000 ………… 4,00,000 ………… 65,000
|
…………. ………….
20,10,000 …………. 26,00,000 ………… 75,000 ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… ………… 3,00,000 ………. 4,00,000 ……….
|
|
| TOTAL | 53,85,000 | 53,85,000 |
This is the exact trial Balance format that should be used
ALSO READ : TRIAL BALACE – तलपट- ट्रायल बैलेंस- परीक्षा सूची – शेष परीक्षण
FAQs on Trial Balance
What is Trial Balance?
Answer: A trial balance is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of ledger accounts. It lists the debit and credit balances from the ledger to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits.
Trial Balance Format
What is the format of a trial balance?
Answer: The trial balance format typically includes columns for the account name, ledger folio, and the debit and credit balances. It can be prepared using the total method (showing total debits and credits) or the balance method (showing only the balances of each account).
What is Trial Balance?
What is a trial balance in accounting?
Answer: In accounting, a trial balance is a statement that shows the debit and credit balances of all ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the recorded transactions. It is prepared after posting journal entries to the ledger.
Trial Balance Meaning
What is the meaning of trial balance?
Answer: The trial balance is a statement that includes all debit and credit balances from the ledger accounts. It is used to verify that the total debits equal the total credits, ensuring the accuracy of the bookkeeping.
Difference Between Trial Balance and Balance Sheet
Question: What is the difference between a trial balance and a balance sheet?
Answer: A trial balance is a statement that lists all ledger account balances to check the accuracy of the bookkeeping, while a balance sheet is a financial statement that shows the company’s financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity, at a specific point in time.
Trial Balance Questions
Question: What types of questions can be asked about a trial balance?
Answer: Questions about a trial balance can include how to prepare it, how to identify and correct errors, the differences between the total and balance methods, and its role in the accounting cycle.
Trial Balance Accounting
Question: How is a trial balance used in accounting?
Answer: In accounting, a trial balance is used to verify the accuracy of the ledger accounts. It ensures that total debits equal total credits, helping to identify any errors in the bookkeeping process before preparing final accounts.
Trial Balance Definition
Question: What is the definition of a trial balance?
Answer: According to J.R. Batliboi, “Trial balance is a statement, prepared with the debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books.”
Types of Trial Balance Errors
Question: What types of errors can a trial balance help identify?
Answer: A trial balance can help identify errors in totaling, balancing ledger accounts, posting incorrect amounts, and partial omissions. However, it may not detect errors of complete commission, wrong recording, complete omission, posting to the wrong account on the correct side, compensating errors, or errors of principle.
Trial Balance Preparation Methods
Question: What are the methods of preparing a trial balance?
Answer: A trial balance can be prepared using two methods:
- Total Method (Gross Trial Balance Method): Lists the total debits and credits of each account.
- Balance Method (Net Trial Balance Method): Lists only the debit or credit balances of each account.
Limitations of Trial Balance
Question: What are the limitations of a trial balance?
Answer: While a trial balance helps ensure the arithmetical accuracy of the books, it does not guarantee the absence of errors, such as errors of omission, commission, principle, or compensating errors. It also does not confirm the correctness of the account balances or the financial statements.
Advantages of Trial Balance
Question: What are the advantages of preparing a trial balance?
Answer: Advantages include verifying arithmetical accuracy, providing a summary of all ledger balances, identifying errors before final accounts preparation, and serving as the basis for preparing financial statements.
Accounts with Debit & Credit Balances (Balance Method – Trial Balance)
| Debit Balance Accounts | Credit Balance Accounts |
|---|---|
| Assets – Cash, Bank, Furniture, Building, Machinery, Goodwill, Bills Receivable, Debtors, Prepaid Expenses, Accrued Income, Fixtures, Motor Vehicles, Computers, etc. | Liabilities – Capital, Creditors, Bills Payable, Loans, Mortgage Loans, Outstanding Expenses, Bank Overdraft, Advance Income, etc. |
| Purchases (always debit) | Sales (always credit) |
| Sales Returns (Return Inwards) | Purchase Returns (Return Outwards) |
| Opening Stock | Reserves – Capital Reserve, General Reserve, Securities Premium Reserve, Investment Fluctuation Reserve, Tax Reserve, Capital Redemption Reserve, Debenture Redemption Reserve, etc. |
| Expenses & Losses – Wages, Salaries, Rent Paid, Trade Expenses, General Expenses, Interest Paid, Commission Paid, Discount Allowed, Interest on Capital, Interest on Loan, Depreciation, Bad Debts, etc. | Incomes & Gains – Rent Received, Interest Received, Commission Received, Discount Received, Interest on Investments, Dividend Received, etc. |
