Table of Contents
Preparation of Journal, Ledger, Trial balance, and Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study:
- Partnership Deed
- 15 transactions
- Journal Entries
- ledger
- Trial Balance
- Trading and Profit and Loss Account
- Profit and Loss Appropriation
- Partner’s Capital Account
- Balance Sheet
Partnership Deed:
A partnership Deed is a written agreement among the partners for managing the affairs of a partnership firm Business.
Definition of partnership Deed
‘Partnership Deed’ is a written statement (Document) that contains the terms and conditions governing the partnership firm’s business.
Every firm can frame its own partnership deed in which the objective of the partnership business, the contribution of capital by each partner, the ratio in which the profits and the losses will be shared by the partners, rights, duties, and liabilities of the partners are stated in detail. It helps in settling up the disputes arising among the partners during the general conduct of partnership business.
Read in Hindi : साझेदारी विलेख/ संलेख
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
Key points of Definition of partnership Deed
- Partnership Deed is an agreement.
- It contains terms and Conditions of the agreement.
- Partnership Deed contains the objective of partnership business.
- It includes agreement on profit sharing ratio.
- It contains the rights, duties, and liabilities of the partners.
- A written form is called ‘partnership deed’
- Partnership Deed is also called ‘ Articles of Partnership’
- It can be oral or written but, writing is considered good.
Also Read: 20 transactions with their Journal Entries, Ledger and Trial balance
Main Contents of Partnership Deed
(i) Name and address of the partnership firm.
(ii) Nature and objectives of the business.
(iii) Name and address of each partner.
(iv) Ratio in which profits and Losses is to be shared.
(v) Capital contribution by each partner.
(vi) Rate of Interest on capital if allowed.
(vii) Salary, bonus, commission or any other remuneration to partners, if allowed.
(viii) Rate of interest on loans and advances by a partner to the firm.
(ix) Drawings of partners and rate of interest charged on drawing.
(x) Method of valuation of goodwill
(xi) Settlement of disputes by arbitration (Mediation);
(xii) Settlement of accounts at the time of retirement or death of a partner.
(xiii) Circumstances (situation or condition) in which the firm can be dissolved.
(xiv) Settlement of accounts at the time of dissolution of a firm.
(xv) Admission of a new partner.
(xvi) revaluation of assets and liabilities on the reconstitution of the partnership i.e. on the admission, retirement or death of a partner;
(xvii) Rights, duties and liabilities of the partners
(xviii) Bank Account Operation.
(xix) Accounting period.
(xx)Period of Partnership (If any)
(xxi) Retirement of a Partner.
(xxii) Any other matter relating to the conduct of business.
Normally, the partnership deed covers all matters affecting the relationship of partners amongst themselves. However, if there is no express agreement on certain matters, the provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 section (13b) shall apply.
Also Read : Meaning and advantages of Double Entry System
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
Accounting rules applicable in the absence of Partnership deed
Provisions of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 are applied ( section 13 b)
- Profit sharing Ratio: Profits and losses would be shared equally among partners.
- Interest on capital: No interest on capital would be allowed to partners. If there is an agreement to allow interest on capital it is to be allowed only in case of profits.
- Interest on drawings: No interest on drawings would be charged from partners drawing.
- Salary, Bonus, Commission: No salary or commission and bonus and any other remuneration are to be allowed to partners.
- Interest on Loan: If a partner has provided any Loan to the firm, he would be paid Interest at the rate of 6% p.a. This interest on the loan is a charge against profits i.e. it is to be allowed even if there are losses to the firm.
- Admission of a new partner: A new Partner can be admitted only with the consent of all the existing (old) partners.
- Right to participate in the business: Each partner has a right to participate in the proceedings of the business.
- Inspection of the accounts of the firm: Each partner has the right to inspect the accounts of the firm and can have a copy of the same.
Note: Any of the above provisions can be changed by the partners after an agreement.
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
Preparation of Journal, Ledger, Trial balance and Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study- 15 Transactions
Mr. Mohit and Mr. Mayank entered into a partnership business and decided to sell computers. Their Partnership Deed is as follows.
Partnership Deed:
- Name of the Firm: Mohit & Brothers
- Name of the partners: Mohit and Mayank
- Capital Contribution:
Mohit will contribute ₹10,00,000.
Mayank will contribute ₹10,00,000. - Profit sharing Ratio: They decided to share profits and losses equally.
- Interest on Capital: Interest is to be allowed on capital @ 5% p.a.
- Interest on Drawing: Interest on drawing is to be charged @ 10% p.a.
- Salary to Partner: No salary allowed.
- Commission/Bonus: Mohit is entitled to a commission of ₹20,000 p.m.
- Each partner can take part in the management and conduct of business.
15 Transactions:
|
Date |
Particulars |
₹ |
| March 1 | Capital Introduced Mohit:
Mayank |
10,00,000
10,00,000 |
| Cash Deposited to bank | 15,00,000 | |
| March 2 | Building purchased
Furniture purchased Computer purchased (For Self Business) Office Equipment purchased Car purchased All of the payment was made by cheque |
5,00,000
50,000 50,000 1,00,000 2,00,000
|
| March 3 | Goods purchased on credit from Technology Warehouse (25 Computers @ Rs.40,0000 Each) | 10,00,000 |
| March 5 | Goods sold for cash (5 Computers) | 2,50,000 |
| March 6 | Goods sold on credit to Gupta Traders (4 Computers) | 3,75,000 |
| March 8 | Cash sales (2 Computers) | 1,00,000 |
| March 9 | Credit sales Ram Traders (3 Computers) | 1,50,000 |
| March 10 | Credit sales to Shyam Traders (3 Computers) | 2,25,000 |
| March 12 | Cash sales (3 Computers) | 1,50,000 |
| March 16 | Cash received from Gupta Traders | 3,75,000 |
| March 17 | Cash Received from Shyam Traders | 2,25,000 |
| March 20 | Cash paid to Technology Warehouse | 5,00,000 |
| March 21 | Advertisement Expenses | 10,000 |
| March 23 | Cash deposited to bank | 5,00,000 |
| March 25 | Rent Paid | 20,000 |
| March 26 | Salary paid by cheque | 30,000 |
| March 28 | Wages paid by cheque | 20,000 |
| March 30 | Manufacturing Expense Paid by Cheque | 25,000 |
| March 31 | Cash withdrawn by Mohit for personal use | 50,000 |
Admission of a partner-Important Questions-2
Journal Entries:
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
Ledger:
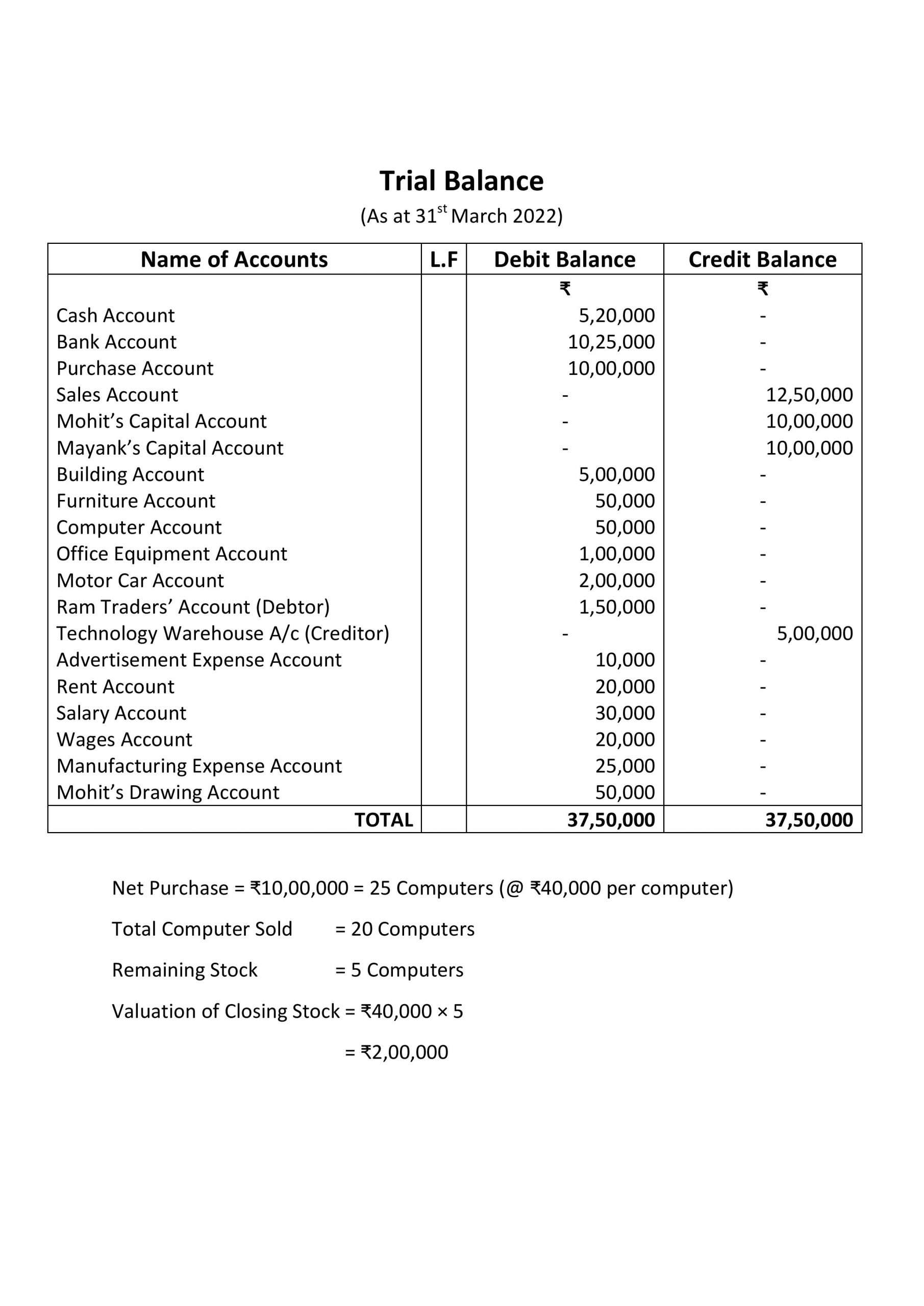
Trial Balance :
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
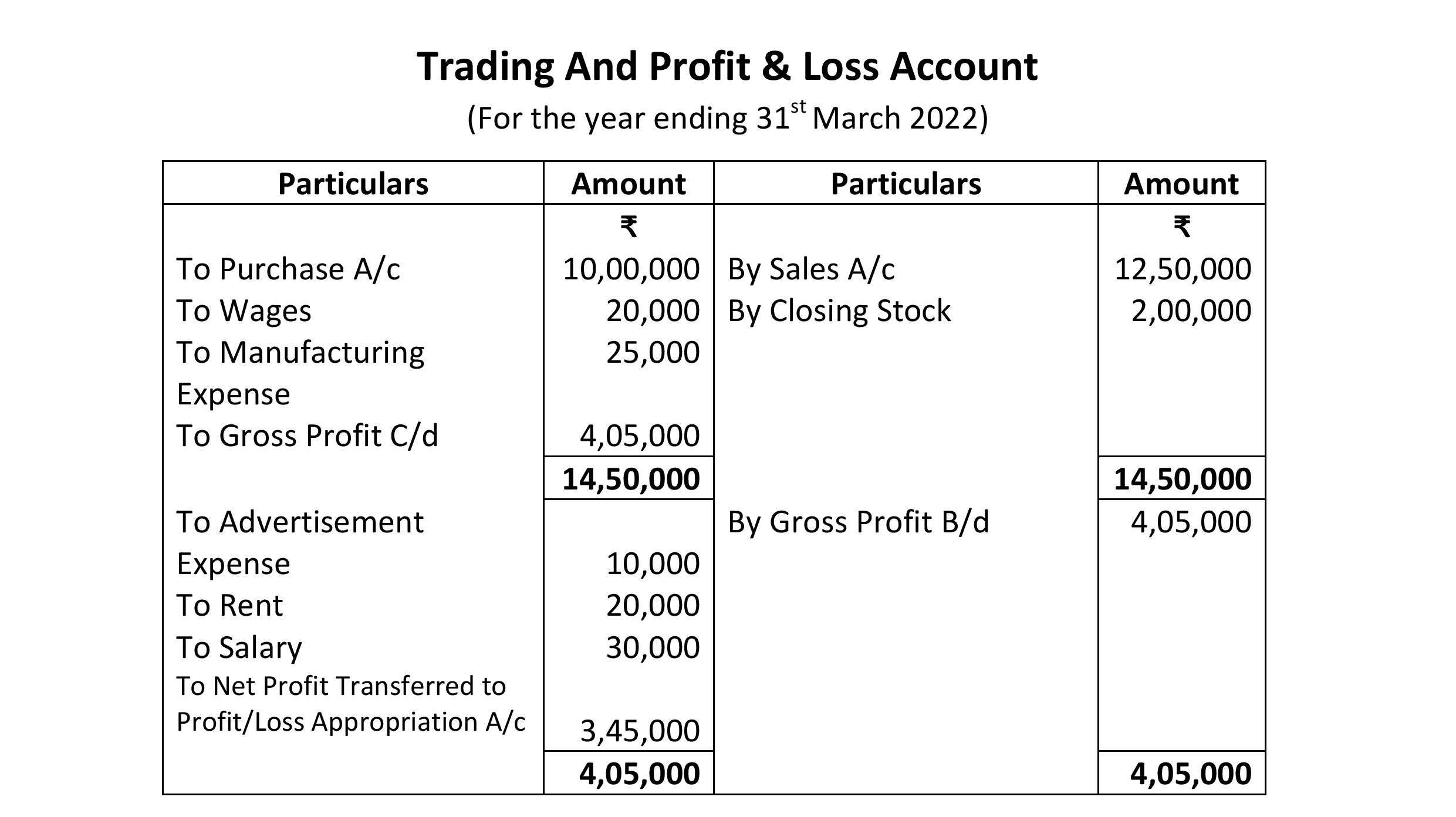
Trading and Profit&Loss Account:
Profit and loss Appropriation Account
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
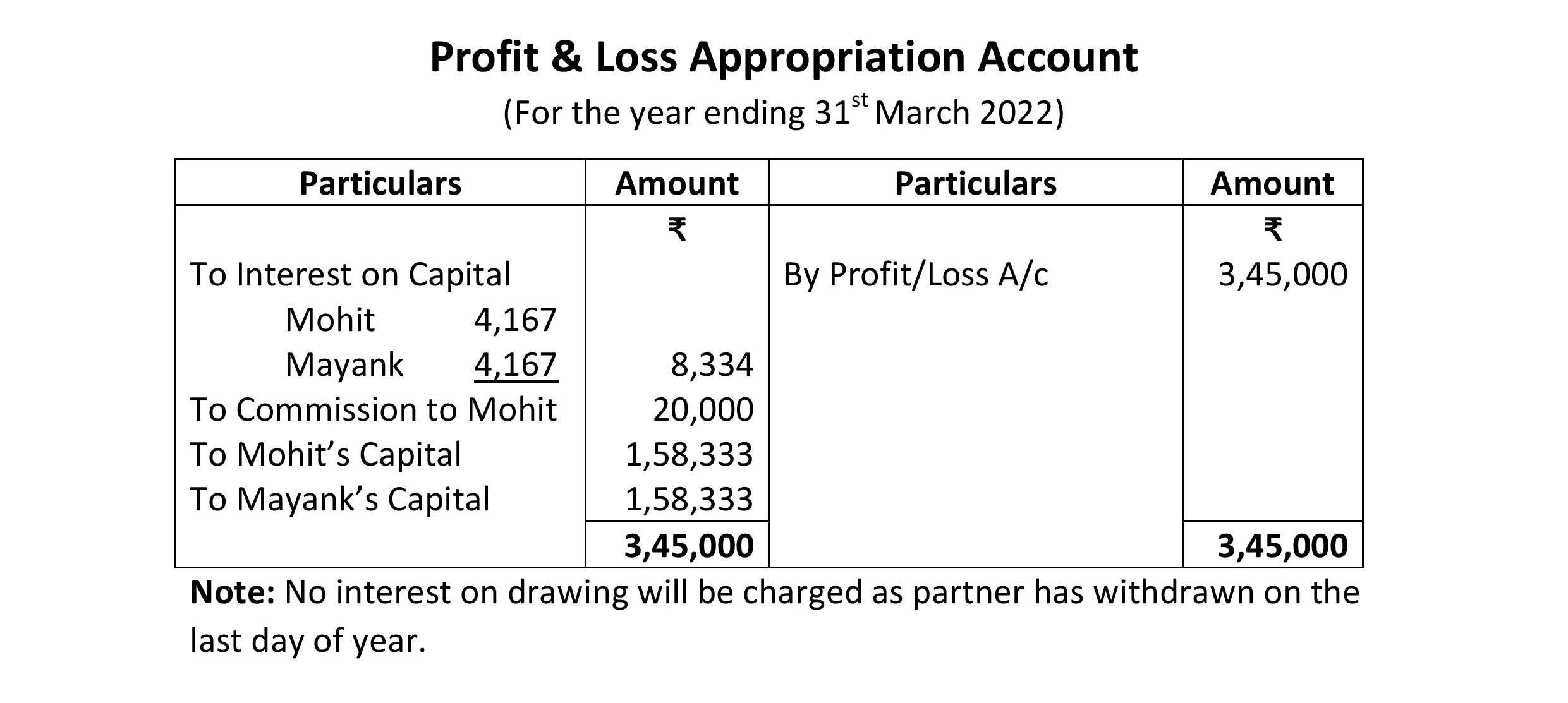
Profit and Loss Appropriation Account:
Journal Entries (For Appropriation)
Note: From 1st March to 31st March, One Month of Interest will be calculated on the Capital Of Mohit and Rachit:
Mohit’s Interest on Capital= 10,00,000X5/100X1/12
= 4,166.66 Or 4,167
Rachit’s Interest on Capital= 10,00,000X5/100X1/12
= 4,166.66 Or 4,167
Format of Profit and loss Appropriation Account
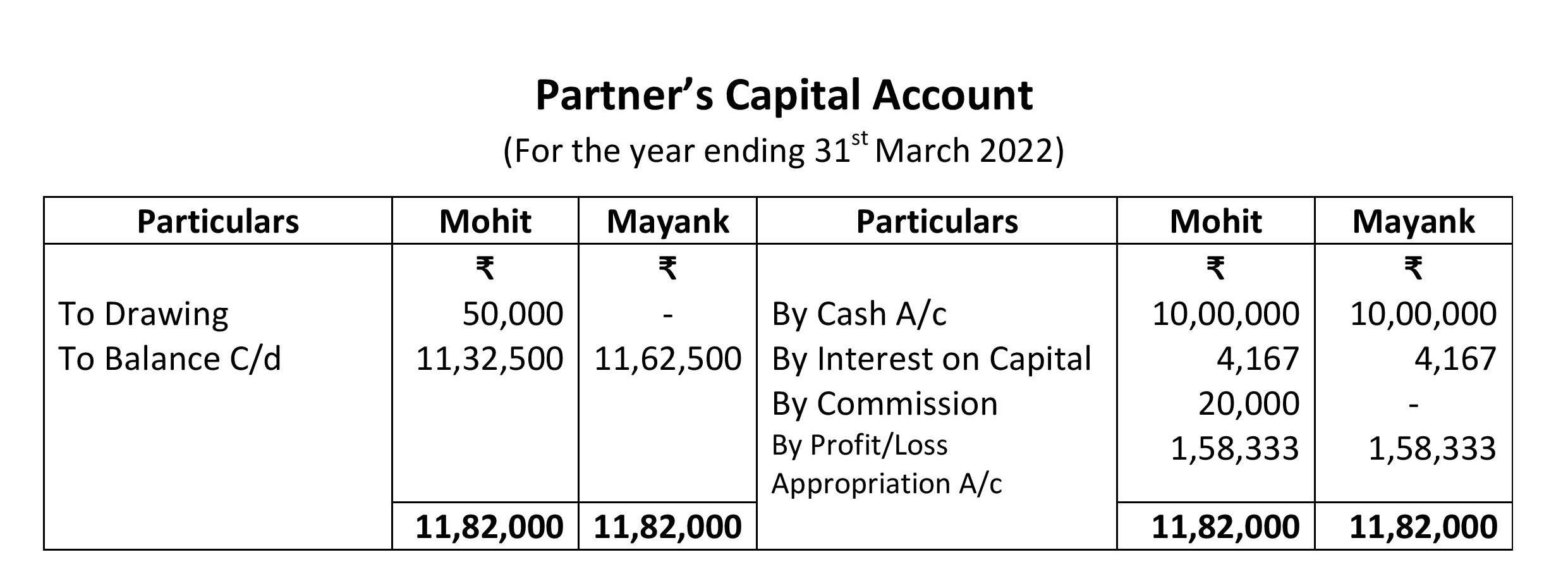
Partner’s Capital Account:
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
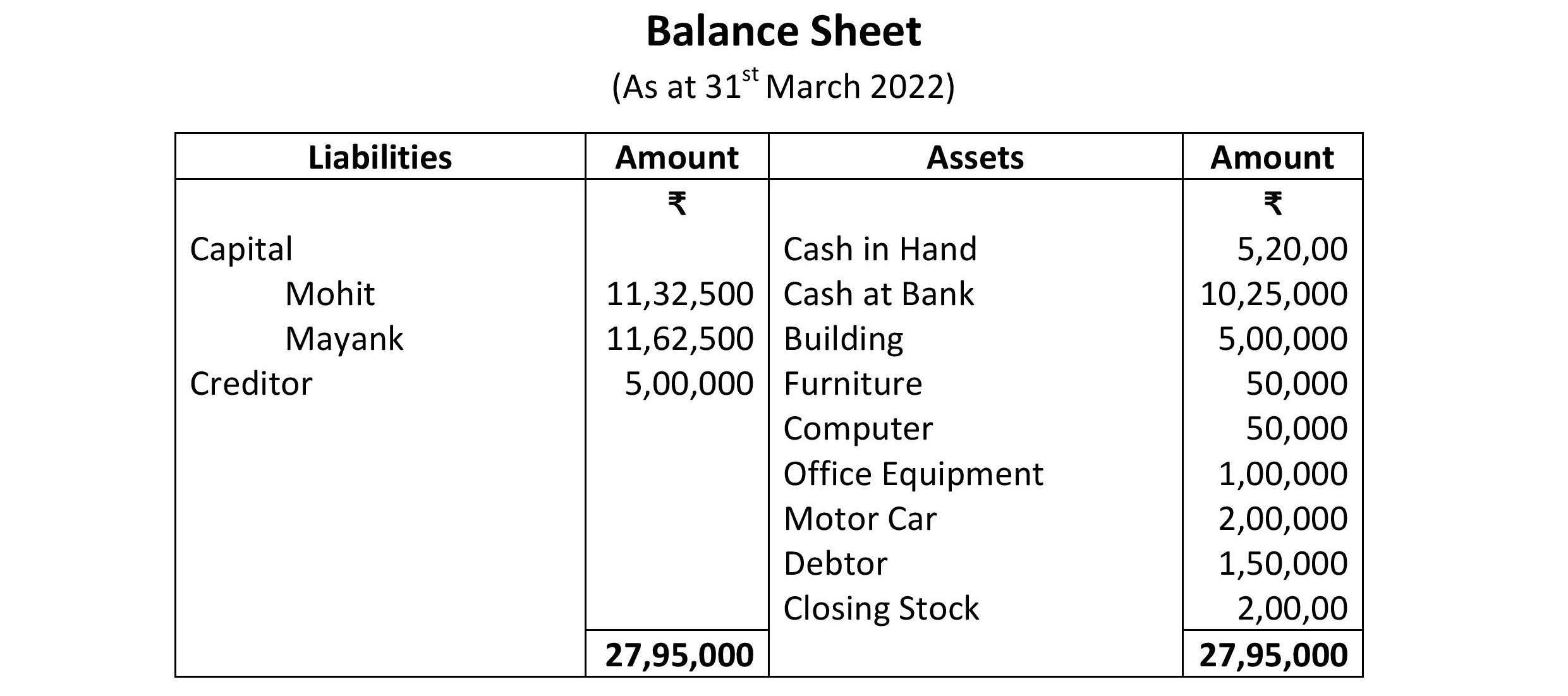
Balance Sheet:
Financial Statements of a partnership firm on the basis of a case study
Admission of a partner-Important Questions-1
Important questions of fundamentals of partnership-3
Hidden Goodwill at the time of Admission of A New Partner
Important questions of fundamentals of partnership
Important questions of fundamentals of partnership-2
Goodwill questions for practice Class 12 ISC & CBSE
Important questions of fundamentals of partnership-5
ACCOUNTING TREATMENT OF GOODWILL AT THE TIME OF ADMISSION OF A NEW PARTNER
Admission of a partner-Important Questions-3










Thank you so much…you’re a true life saver! This helped me incredibly whilst doing my ISC Accounts Projects…
God Bless!;-)
Thank You Sir 🙏
This article is too helpful……
This article is salient…
Truly grateful Sir.! 🙂
Sir can you plz give the bar presentation
Hello mera ek doubt ha balance sheet pe yeh cash in hand and cash at bank kaha se aya question pe nhi ha
cash in hand represent the (Balance of cash Account) and cash at bank represent the (Balance of Bank Account)
Hello ye IOC 4167 kese aya Or
Ye Capital a/c toh balance hi nhi hua hai
Note: From 1st March to 31st March, One Month of Interest will be calculated on the Capital Of Mohit and Rachit:
Mohit’s Interest on Capital= 10,00,000X5/100X1/12
= 4,166.66 Or 4,167
Rachit’s Interest on Capital= 10,00,000X5/100X1/12
= 4,166.66 Or 4,167
Sir ye closing stock kese aya firr
See the working note below the trial balance
And sir yeh capital account to balance hi nhi ha
Sir closing stock kese aya
See the working note below the trial balance
Sir closing stock kese nikala hai coz kitne computer purchase kiya aur kitna sell vo toh mention hi nahi hai
Go through the Question carefully and Analyze
How you got closing stock
See the working note below the trial balance
Thank You Sir ❤️,
Article is easy to understand and helped us too.